Querying: Faceted (Aggregation) Search
When displaying a large amount of data, paging is often used to make viewing the data manageable. It's also useful to give some context of the entire data-set and a easy way to drill-down into particular categories. The common approach to doing this is a "faceted search", as shown in the image below. Note how the count of each category within the current search is across the top.
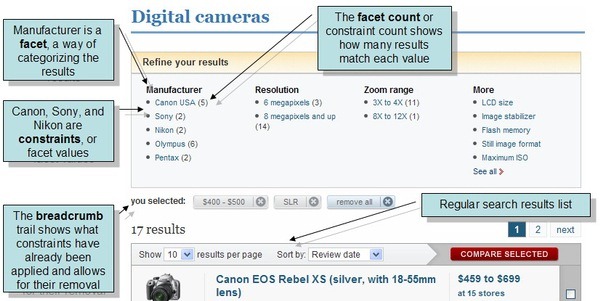
Let's start with defining a document like this:
export class Camera {
constructor(manufacturer, model, {
dateOfListing,
cost,
zoom,
megapixels,
imageStabilizer
}) {
this.manufacturer = manufacturer;
this.model = model;
this.dateOfListing = dateOfListing;
this.cost = cost;
this.zoom = zoom;
this.megapixels = megapixels;
this.imageStabilizer = imageStabilizer;
}
}Step 1
Create an index to work against.
class Cameras_ByManufacturerModelCostDateOfListingAndMegapixels extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
constructor() {
super();
this.map = `from camera in docs.Cameras select new {
camera.manufacturer,
camera.model,
camera.cost,
camera.dateOfListing,
camera.megapixels
}`;
}
}Step 2
Setup your facet definitions:
const facet1 = new Facet();
facet1.fieldName = "manufacturer";
const facet2 = new RangeFacet();
facet2.ranges = [
"cost <= 200",
"cost between 200 and 400",
"cost between 400 and 600",
"cost between 600 and 800",
"cost >= 800"
];
const facet3 = new RangeFacet();
facet3.ranges = [
"megapixels < 3",
"megapixels between 3 and 7",
"megapixels between 7 and 10",
"megapixels >= 10"
];
const facets = [ facet1 ];
const rangeFacets = [ facet2, facet3 ];This tells RavenDB that you would like to get the following facets:
-
For the manufacturer field, look at the documents and return a count for each unique Term found.
-
For the cost field, return the count of the following ranges:
- cost < 200.0
- 200.0 <= cost < 400.0
- 400.0 <= cost < 600.0
- 600.0 <= cost < 800.0
- cost >= 800.0
-
For the megapixels field, return the count of the following ranges:
- megapixels <= 3.0
- 3.0 <= megapixels < 7.0
- 7.0 <= megapixels < 10.0
- megapixels >= 10.0
Step 3
You can write the following code to get back the data below:
const facetResults = await session
.query({ indexName: "Cameras/ByManufacturerModelCostDateOfListingAndMegapixels" })
.whereBetween("cost", 100, 300)
.aggregateBy(facets)
.execute();const facet1 = new Facet();
facet1.fieldName = "manufacturer";
const facet2 = new RangeFacet();
facet2.ranges = [
"cost <= 200",
"cost between 200 and 400",
"cost between 400 and 600",
"cost between 600 and 800",
"cost >= 800"
];
const facet3 = new RangeFacet();
facet3.ranges = [
"megapixels < 3",
"megapixels between 3 and 7",
"megapixels between 7 and 10",
"megapixels >= 10"
];
const facets = [ facet1 ];
const rangeFacets = [ facet2, facet3 ];from index 'Cameras/ByManufacturerModelCostDateOfListingAndMegapixels'
where cost between 100 and 300
select facet(manufacturer), facet(cost <= 200, cost between 200 and 400, cost between 400 and 600, cost between 600 and 800, cost >= 800), facet(megapixels <= 3, megapixels between 3 and 7, megapixels between 7 and 10, megapixels >= 10)This data represents the sample faceted data that satisfies the above query:
[
{
"Name": "manufacturer",
"Values": [
{
"Count": 1,
"Range": "canon"
},
{
"Count": 2,
"Range": "jessops"
},
{
"Count": 1,
"Range": "nikon"
},
{
"Count": 1,
"Range": "phillips"
},
{
"Count": 3,
"Range": "sony"
}
]
},
{
"Name": "cost",
"Values": [
{
"Count": 6,
"Range": "cost <= 200"
},
{
"Count": 2,
"Range": "cost between 200 and 400"
},
{
"Count": 0,
"Range": "cost between 400 and 600"
},
{
"Count": 0,
"Range": "cost between 600 and 800"
},
{
"Count": 0,
"Range": "cost >= 800"
}
]
},
{
"Name": "megapixels",
"Values": [
{
"Count": 0,
"Range": "megapixels <= 3"
},
{
"Count": 6,
"Range": "megapixels between 3 and 7"
},
{
"Count": 1,
"Range": "megapixels between 7 and 10"
},
{
"Count": 1,
"Range": "megapixels >= 10"
}
]
}
]Storing Facets
If you do not have to change your facets dynamically, you can store your facets as a FacetSetup document and pass the document ID instead of the list each time:
const facetSetup = new FacetSetup();
facetSetup.facets = facets;
facetSetup.rangeFacets = rangeFacets;
await session.store(facetSetup, "facets/CameraFacets");const facetResults = await session
.query({ indexName: "Cameras/ByManufacturerModelCostDateOfListingAndMegapixels" })
.whereBetween("cost", 100, 300)
.aggregateUsing("facets/CameraFacets")
.execute();const facet1 = new Facet();
facet1.fieldName = "manufacturer";
const facet2 = new RangeFacet();
facet2.ranges = [
"cost <= 200",
"cost between 200 and 400",
"cost between 400 and 600",
"cost between 600 and 800",
"cost >= 800"
];
const facet3 = new RangeFacet();
facet3.ranges = [
"megapixels < 3",
"megapixels between 3 and 7",
"megapixels between 7 and 10",
"megapixels >= 10"
];
const facets = [ facet1 ];
const rangeFacets = [ facet2, facet3 ];from index 'Cameras/ByManufacturerModelCostDateOfListingAndMegapixels'
where cost between 100 and 300
select facet(id('facets/CameraFacets'))Stale Results
The faceted search does not take into account a staleness of an index. You can wait for non stale results by customizing your query with the waitForNonStaleResults() method.
Fluent API
As an alternative for creating a list of facets and passing it to the aggregateBy() method, RavenDB also exposes a dynamic API where you can create your facets using a builder. You can read more about those methods in our dedicated Client API article here.