Cluster Observer
-
The Cluster Observer is a supervising component in the cluster.
It monitors the nodes health and adjusts the nodes state in the Database Group accordingly. -
For each database, it sets the nodes state within the Database Group, thus determining the Database Group Topology.
-
The Observer is always running on the
Leadernode, it requires a consensus to operate.
If there is no Leader, no Database Group Topology decisions can be made. -
In this page:
Note:
-
Don't confuse the Database Group Topology with the Cluster Topology
-
For more info about node types and states in the Cluster see Cluster View
For more info about node types and states in the Database Group see Database Group
The Observer Log
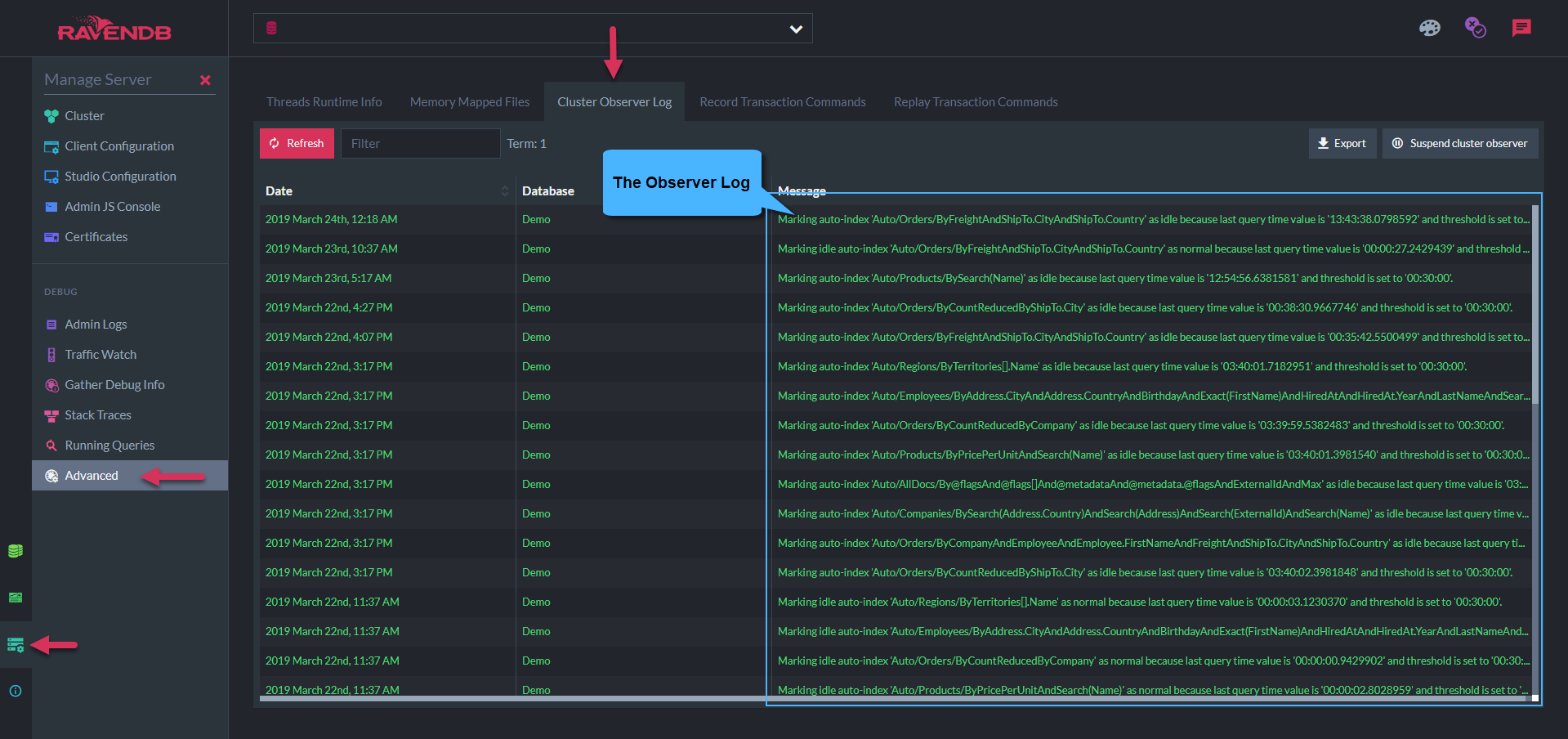
The Observer Log
Observer Log Data
Log Data
1. Refreshing Data
Click Refresh to get latest actions performed by the Observer
When a new Leader is elected:
Termvalue will increase- The Observer will move and run on the new Leader
- All previous log data will not be kept - clicking
Refreshwill start a new log
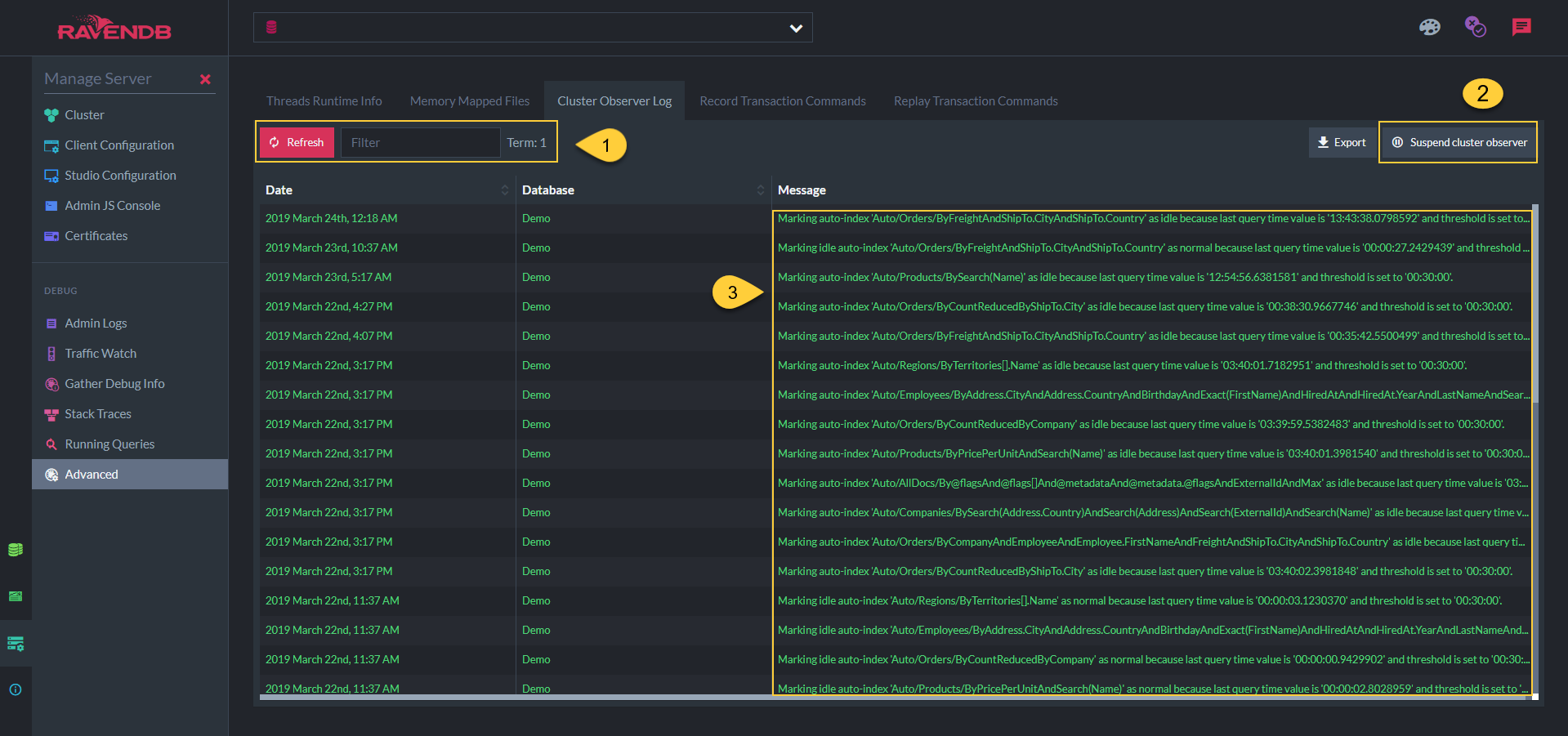
2. Suspending the Cluster Observer
Be careful with this option
- Use this only when you don't want the Observer to make any changes to the Database Group Topology
i.e. when taking nodes down for maintenance
3. States Flow
When a new node is added to a Database Group:
-
The Observer will add the node as
Promotable. -
Once the node has caught up with the state of the Database Group, fully updated with the database data and finished indexing the last data sent to it, the Observer will promote it to a full
Member.
For a detailed explanation of a Member actions and tasks within a database group see Database Group
When the Observer notices that a node is down ,or unresponsive, it will:
-
Set the node to a
Rehabstate. -
If 'Allow Dynamic Database Distribution' is set (see Create Database),
then after a pre-configured time period, the Observer will add another node from the cluster to the Database Group in order to keep the replication factor.
The replacement node will be set toPromotableand will start catching up data from the other nodes in the group. -
The Observer will Update the Database Group Topology with these changes so that each node in the Database Group will re-calculate his work assignments.
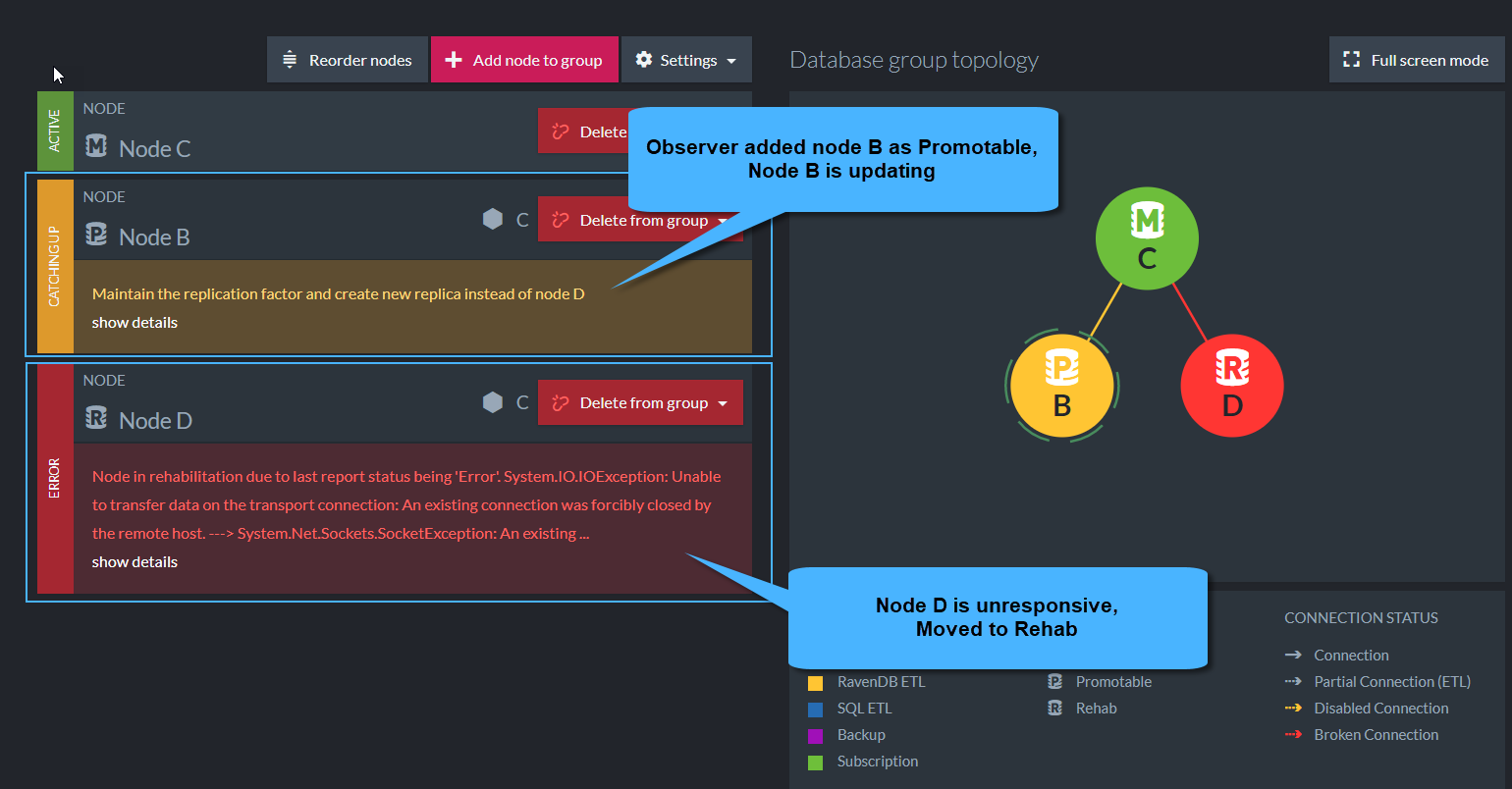
Node D is down - Node B is replacing
When the Rehab node is responsive again:
1. If a replacement node was added when the node was down: (Dynamic Database distribution was set)
-
If the replacing node is fully updated (in a
Memberstate)
then the Observer will delete the node that came back from the Database Group Topology. -
If the replacing node is still Not fully updated (still in
Promotablestate)
then the Observer will set theRehabnode toPromotableso that it starts updating.
At this point the replication factor is greater than was set for the relevant database,
so the Observer will go ahead and delete the extra node, either the replacement one or the Rehab one - whoever is the last to be fully updated. -
Either way, deletion of a node will not occur before the Observer verifies that all data to be deleted from the node was replicated to the Database Group members.
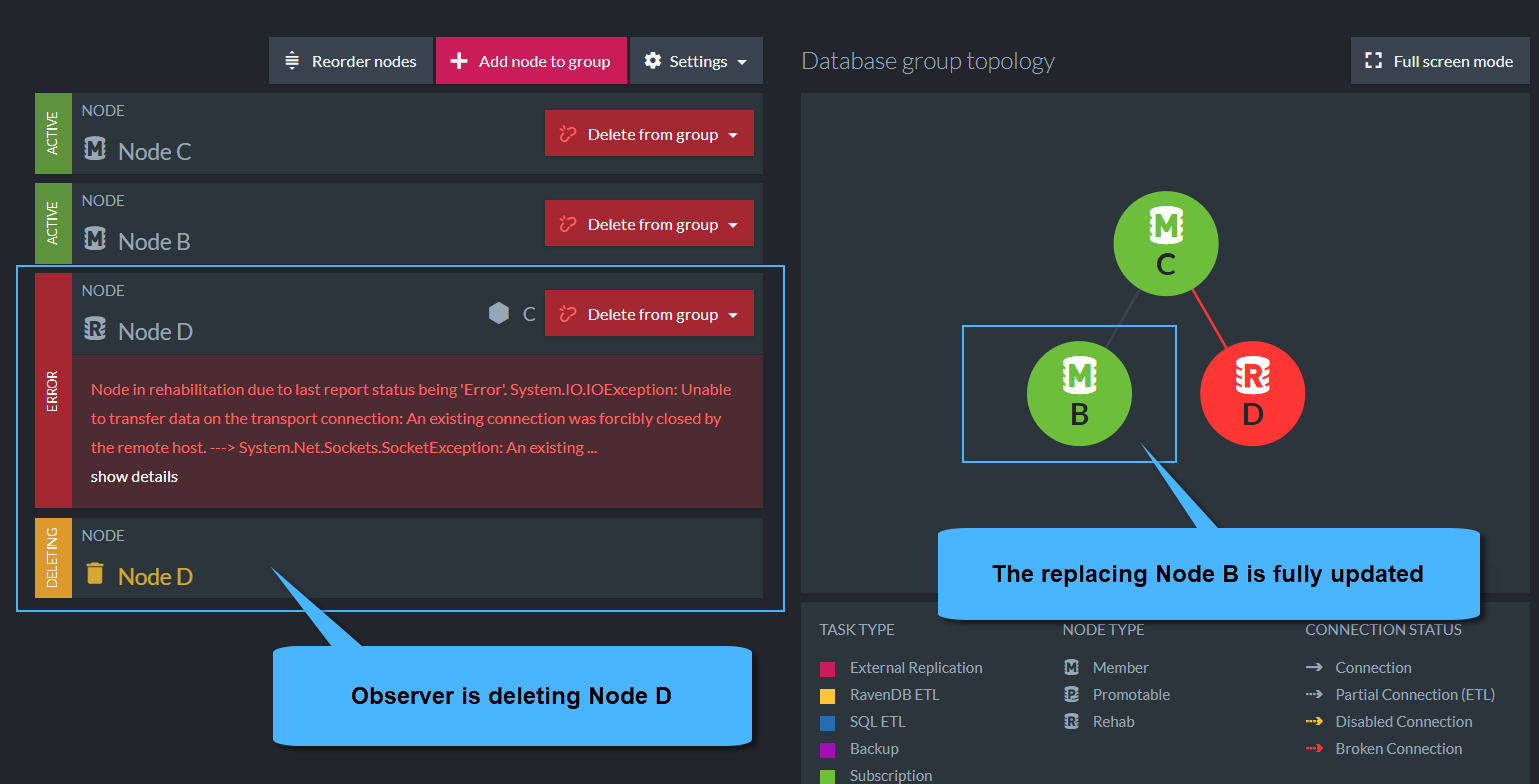
Node B is fully updated - Deleting Node D
2. If no replacement node was added: (Dynamic Database Distribution was not set)
-
The
Rehabnode will start catching up data from the other members in the relevant Databases Groups.
(Note: the node can be part of multiple Databases Groups...) -
Once it is fully updated, the Observer will directly promote it to a full
Memberin the Database Group Topology.