Cluster View
-
A RavenDB Cluster is one or more machines (nodes) that have been joined together, working to achieve the same goal.
-
Using the Raft consensus protocol, the cluster distributes work among the various nodes, handles failures, recovery, and more.
The cluster Member nodes elect a Leader - a node that manages the cluster state. -
This view shows your cluster's current state and structure.
-
You can manage the cluster by actions such as:
- Adding a node to the cluster
- Changing the Leader
- Reassigning cores
- And much more
-
In this page:
Cluster View Stats
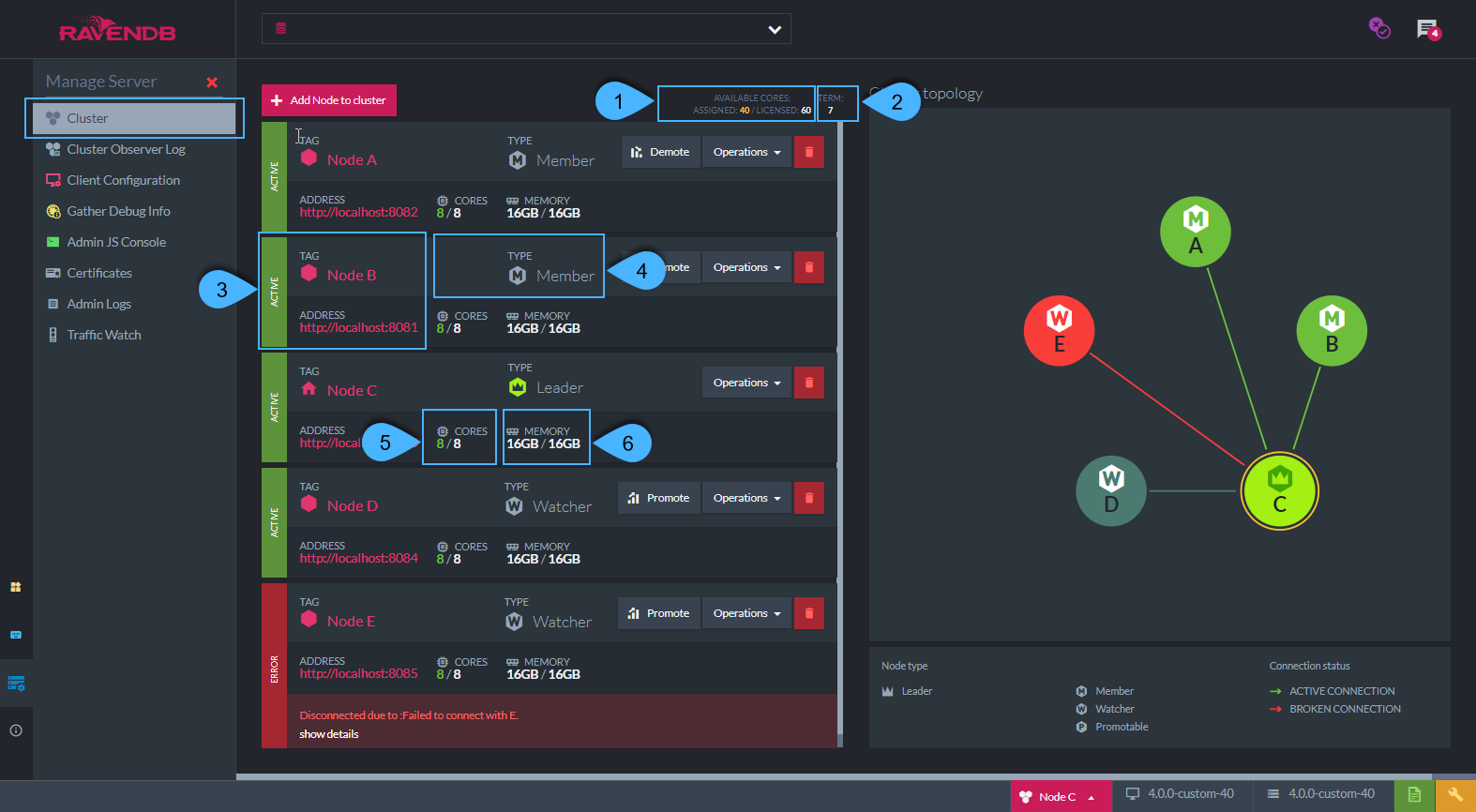
Cluster Stats
- Available Cores
Assigned: Total number of cores assigned to use for server nodes in all of the cluster
Licensed: Total number of cores available for usage according to your license - per the whole cluster - Term
Number of times that elections occurred in the cluster -
Node State, Tag, and Address:
A node state can be one of the following:- Passive - Node doesn't belong to any cluster
- Active - Node is a fully functional member in the cluster
- Error - Node is down or not reachable
- Voting - Elections for a new Leader are taking place
- Waiting - This is the state of a Watcher when the other members are in a voting process
-
Node Type
A node type can be one of the following: (See a more detailed explanation below)- Member (Note: A Leader is a special member)
- Watcher
- Promotable
- Cores Info
Number of cores assigned for the node to use - out of available cores on this node's machine -
Memory
Memory used by the node out of total memory installed on this node's machine.
The core-memory ratio is determined by your license type
Cluster View Operations
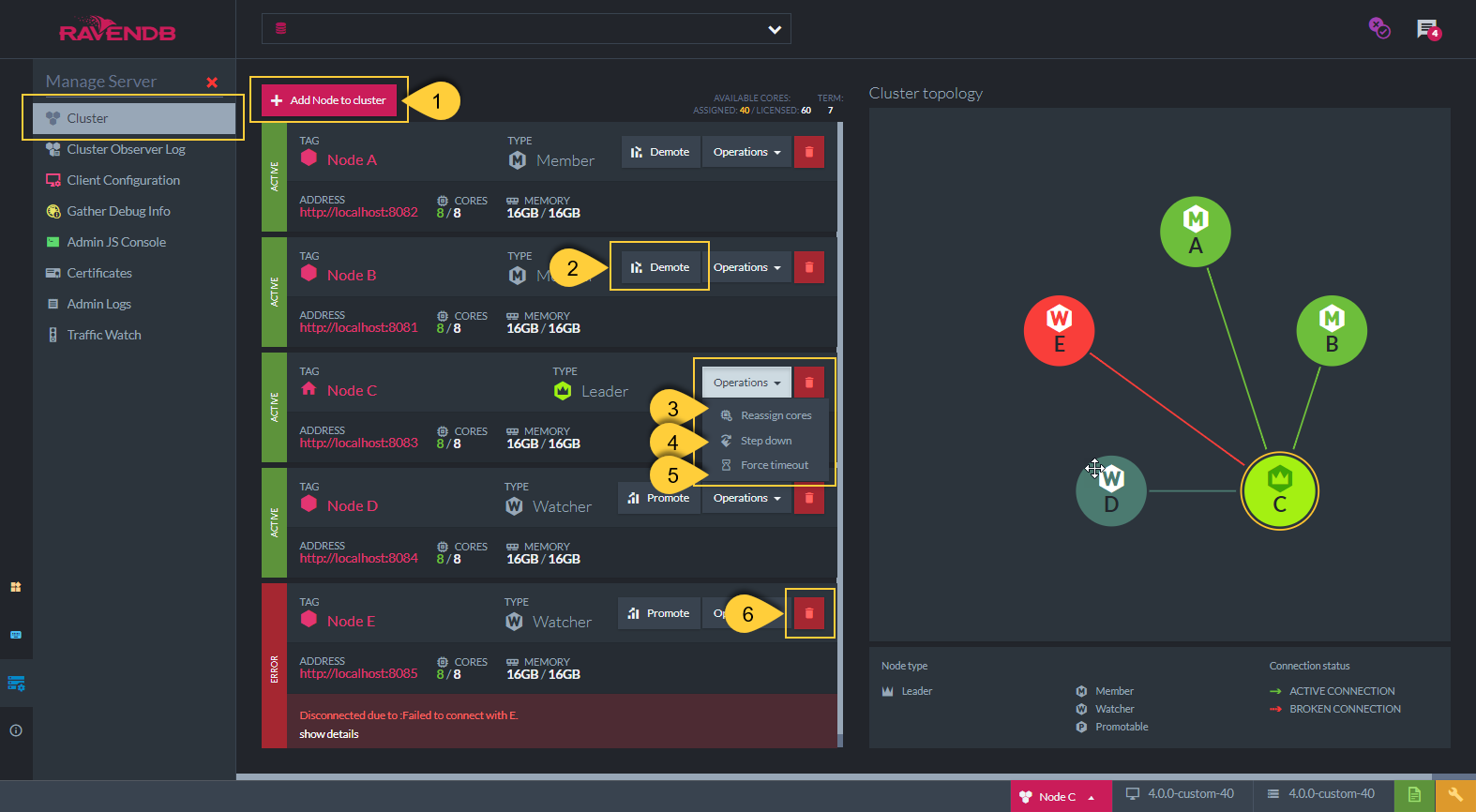
Cluster Operations
- Add New Node to Cluster
See Add node to cluster - Demote
Demote a Member to be a Watcher - Reassign Cores
Reassign the number of cores to be used by the server on this node - Step Down
This option is available only on the Leader node
A new voting process will be triggered and a new Leader will be elected - Force Timeout
The default configuration for the RavenDB cluster is that each node expects to get a heartbeat from the cluster leader
(default: every 300 milliseconds).
Clicking 'Force Timeout' will trigger actions on the node as if it did not hear from the Leader in this time period. - Remove Node from Cluster
Remove the node from the cluster. Note: The server on this node is not shut down.
Reassign Cores
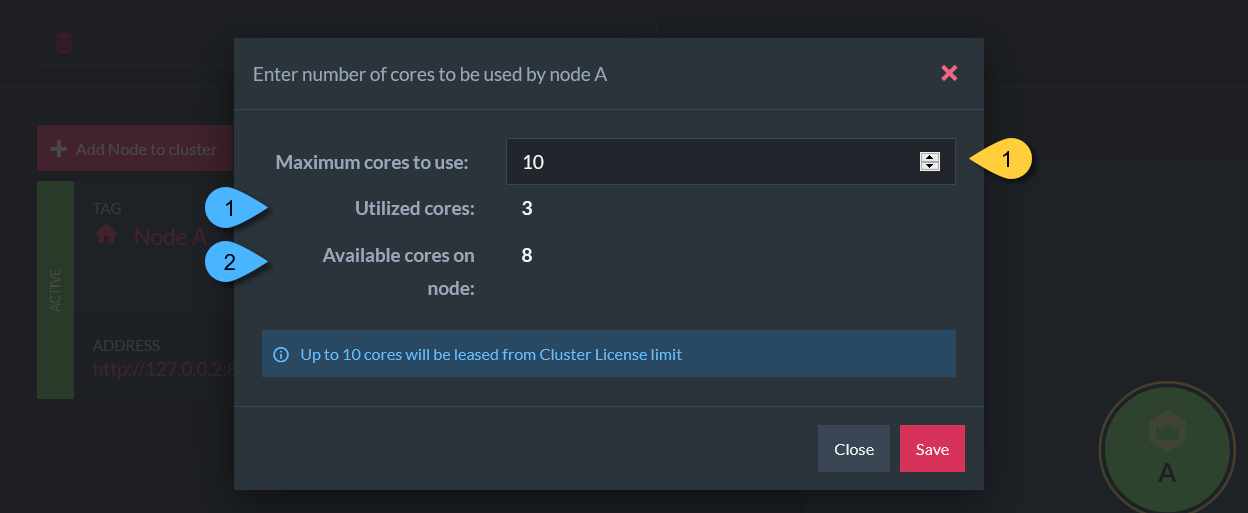
Reassign Cores
1. Set a maximum number of cores that can be used by this node
1. Number of cores this node is currently using
2. Number of available cores on this node's machine
Learn more in Add Node to Cluster.
Cluster Nodes Types
-
Member
- A Member is a fully functional voting member in the cluster
-
Leader
- A Leader is a Member
- The Leader is responsible for monitoring the cluster's health, making sure that decisions making is consistent at the cluster level,
as long as a majority of the nodes are functioning and can talk to one another. For example, the decision to add a database to a node will be either accepted by the entire cluster (eventually) or fail to register altogether. - The Leader maintains the database topology, which is fetched by the clients as part of their initialization.
- Cluster-wide operations can't be done when the Leader is down.
-
Watcher
- A Watcher is a non-voting node in the cluster that is still fully managed by the cluster.
- A Watcher can be assigned databases and work to be done.
- Grow your RavenDB cluster by adding Watchers without suffering from large voting majorities and the latencies they can incur, as these nodes don't take part in majority calculations and are only there to watch what's going on in the cluster. So cluster decisions can be made with a small majority of nodes while the actual size of the cluster can be much higher.
- Any number of Watchers can be added to handle the workload.
-
Promotable
- Promotable is a pre-state before becoming a Watcher or a Member.
- Cannot make cluster decisions (i.e vote for leader, enter a new Raft command to the log).
- Updated by the leader to the latest Raft state.
Cluster Nodes States & Types Flow
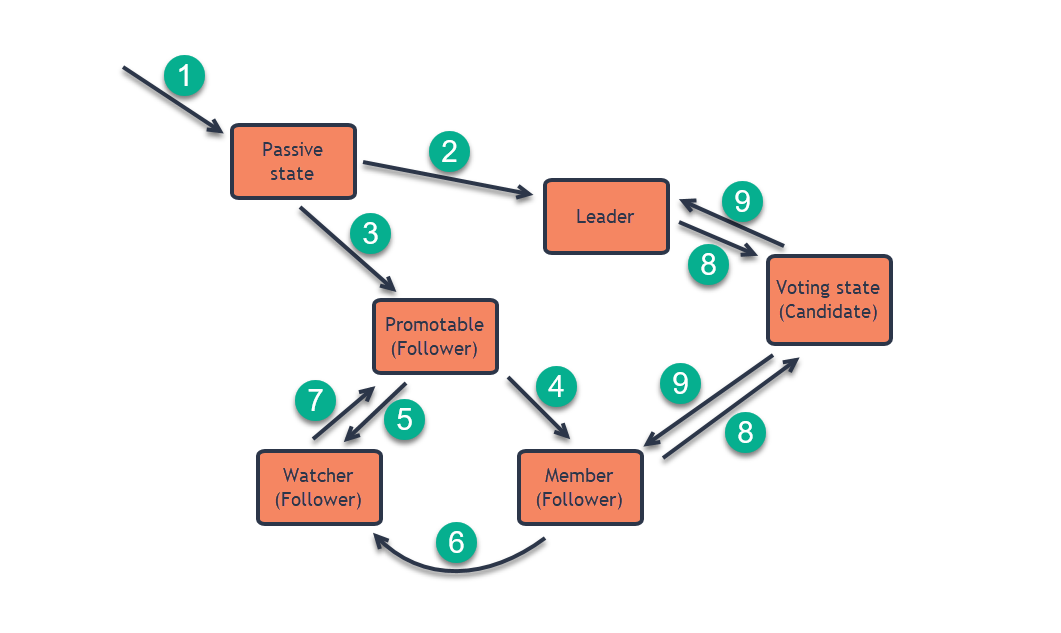
States Flow
-
1. A new server/node will start as Passive, meaning it is not part of any cluster yet.
Learn how to add a node to a cluster in: Adding a Node to a Cluster. -
2. When a node is added to a cluster, it immediately becomes the Leader if it is the only node in the cluster.
-
3. When a node is added to a cluster and a Leader already exists,
it will become Promotable (on its way to either becoming a Member or a Watcher - depending on what was specified when created.) -
4. A node will become a Member of the cluster if not specified otherwise.
-
5. A node will become a Watcher if specified when adding the node.
-
6. A Member can be
Demotedto a Watcher. -
7. A Watcher can be
Promotedto a Member. It will first become Promotable and a Member thereafter. -
8. A Member (a regular Member or a Leader - but not a Watcher) can become a Candidate when a voting process for a new Leader takes place.
Elections can occur when:
Step Downis clicked on the LeaderForce Timeoutwas clicked-
The Leader node is down for some reason
9. When the voting is over and a new Leader is elected, one node will become a Leader and the rest will go back to being Members.
- A Watcher does not take part in the voting process.
- During elections, a Watcher enters a waiting state until elections are over.
Cluster-Wide operation -vs- Database Operations
Operations in RavenDB are usually divided into cluster-wide operations and internal database operations.
Cluster-Wide Operation
- Any action/decision that is made at the cluster level and needs a Raft consensus (so that the cluster is always kept consistent).
- This decision will either be accepted by the entire cluster or completely fail to register.
Note: An action is accepted by the entire cluster if a majority of the nodes have approved that action - if a majority of the nodes isn't available, we can't proceed. -
i.e.:
- Creating/deleting/enabling/disabling a database
- Creating/deleting/modifying/enabling/disabling an ongoing task
- Creating/deleting/modifying an index
Database Operation
- Database operation can always be done on a node (even in the case of a cluster partition)
- Database operation only impacts that particular database
- Any such update is automatically replicated to all other nodes in the Database Group
-
i.e.:
- Any Read/Write operation on a database such as:
- Create/Delete/Update a document, attachment or revision
- Performing a query