Indexes List View
-
All the database indexes are listed in this view.
-
Actions such as creating a new index, modifying an existing index, setting its desired state, and much more can be performed.
-
In this page:
Indexes List View
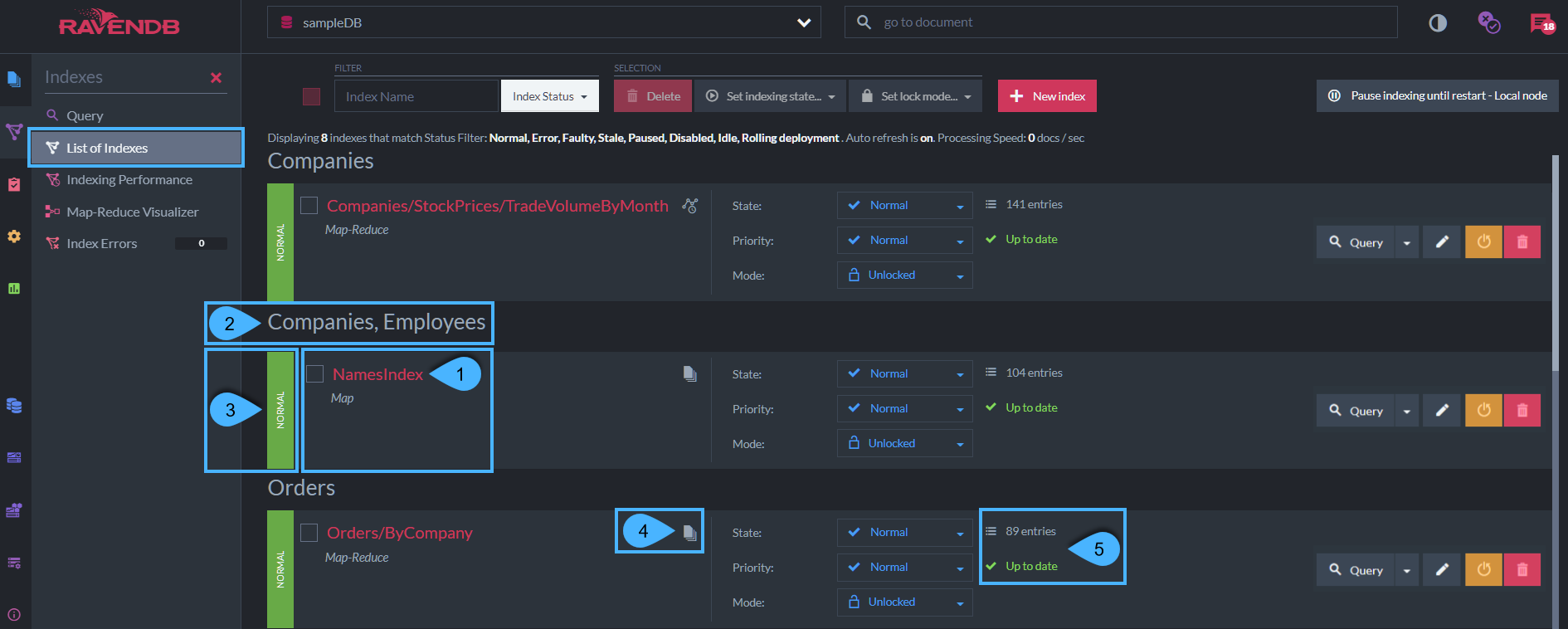
Figure-1: The indexes List View
1. Index name and type
Name- e.g. In the above example the index name is: 'NamesIndex'.-
Type- This is the Index Type, which can be -- Map
- Map-Reduce
- Auto Map
- Auto Map-Reduce
- JavaScript Map
- JavaScript Map-Reduce
2. Collections
- These are the collections that are defined in the Map part of the index-definition.
- Data from these collections is scanned and indexed.
- A simple
Map-indexoperates on a single collection while aMulti-Map indexis defined with more than one collection. - In the above example - Index 'NamesIndex' is a Multi-Map index operating on 'Companies, Employees' collections.
3. Index State
-
Normal
The index is active, any new data is indexed. -
Paused- New data is not being indexed.
- Queries will be stale as new data is not indexed.
-
The indexing process will resume upon either of the following:
- Setting 'Resume indexing'
- Restarting the server
- Reloading the database (by disabling-enabling the database).
- Resume indexing from the client code. See resume index.
-
Disabled- New data is not being indexed.
- Queries will be stale as new data is not indexed.
- The indexing process will resume only when setting 'Enable indexing'.
It will Not automatically resume upon restarting the server or reloading the database. - Can also resume indexing from the client code. See enable index.
-
Idle- An auto-index becomes idle when the time difference between its last-query-time and
the most recent time the database was queried on (with any other index) is greater than a configurable threshold (30 min by default).
This is done in order to avoid marking indexes as idle for databases that were offline for a long period of time -
not having new data to index and not queried in general, as well as for databases that were just restored from a snapshot or a backup. - The auto-index will resume its work and go back to the 'Normal' state upon a new query or when resetting the index.
If not resumed, the idle auto-index will be deleted by the server after a configurable time period (72 hrs default).
- An auto-index becomes idle when the time difference between its last-query-time and
the most recent time the database was queried on (with any other index) is greater than a configurable threshold (30 min by default).
-
Error- A malformed indexing-function or missing/corrupted document data will result in an indexing error.
- See more below.
-
Faulty- An index will be 'Faulty' if its data files are corrupted or if not accessible.
- See more below.
4. Index Source
- Can be: Documents | Counters | TimeSeries
5. Index Status
Entries- The number of documents that are the result for a basic query on this index. (e.g. from index 'NamesIndex')Status- Indicate if the index is up-to-date or if it is stale.
Indexes List View - Actions
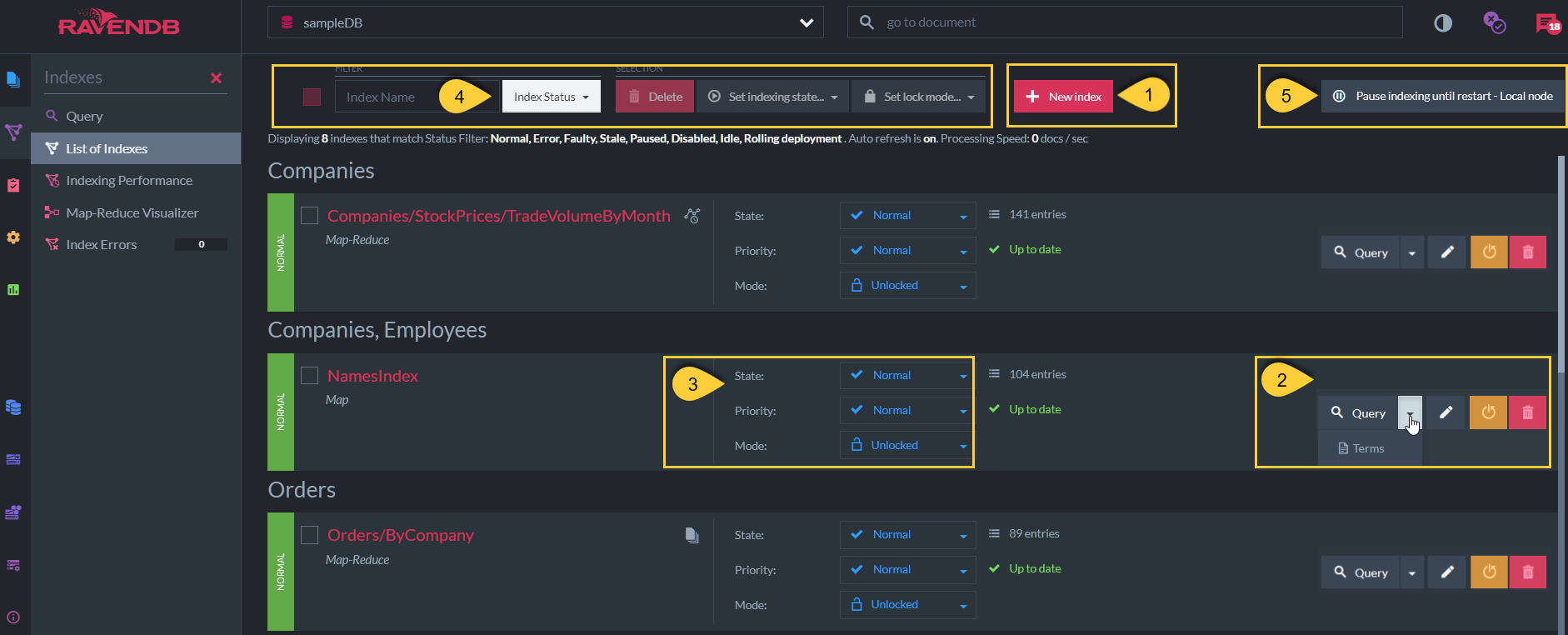
Figure-2: Indexes List View - Actions
1. Crate a new index
- See more in Create New Index.
2. >
- Query
Click to query the index. - Terms
Click to view the index's terms that were actually indexed. -
Edit/View Index
Click to edit/view the index definition.- Static-index: View and edit the index definition.
- Auto-Index: View only.
-
Reset Index
Click to reset the index.
All documents matched by the index definition will be re-indexed.
Resetting the index will resume/enable the normal operation of a paused/disabled index on this node. -
Delete
Click to delete the index.
3. >
- State
Disable index or set as Paused.
The index will stop indexing on the local node the browser is opened on.
See states explanation above (under Figure-1). - Priority
Set the indexing-process thread priority as RavenDB prioritizes requests-processing over indexing by default. -
Mode
Set modifications behavior (static-indexes only):- Unlocked - Changes to the index definitions will be applied. See Side by Side Indexing.
- Locked - Index definitions changes will not be applied! No Error will be raised.
- Locked(Error) - Index definitions changes will not be applied! An error is raised upon trying to modify.
4. Selected Indexes Options
-
Can apply the following for selected/checked indexes from the list:
- Delete
- Set indexes state (disable/pause)
- Set lock mode
5. Pause Indexing until Restart
- Setting this will pause indexing for all indexes in the current database.
- Indexing will be paused only on the local node the browser is opened on.
-
Indexing will resume with either of the following:
- Click this button again ("Resume indexing")
- Restart the server
- Reload the database (by disabling and then enabling the database state)
- Resume indexing from the client code. See resume indexing.
Indexes List View - Errors
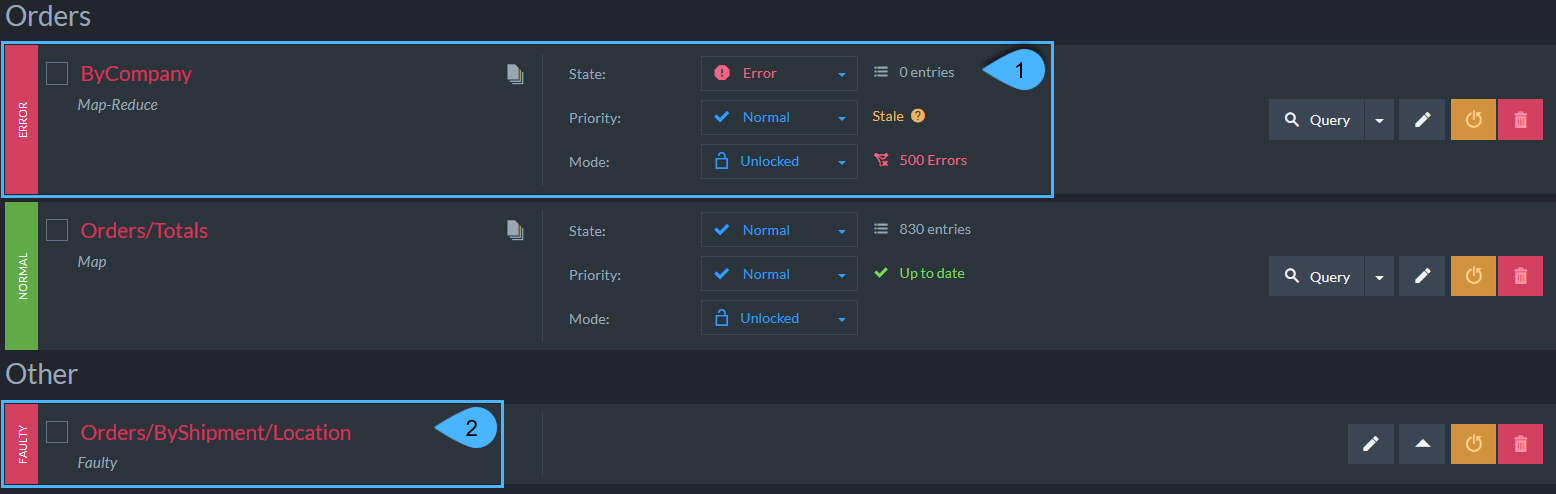
Figure-3: Indexes List View - Errors
1. Errored Index
-
An indexing error can occur when the indexing-function is malformed or when the document data is corrupted/missing.
Once the index errors rate exceeds a certain rate, the index state will be marked with 'Error' and queries can't be made to it. -
Resetting the index will re-index all documents matching its definition and clear the previous errors.
-
In the above example, Index 'Cities/Details' state is 'Error' as 500 errors were encountered.
See more in Degugging Index Errors
2. Faulty Index
-
When an index is already defined but the server fails to open its index data file from disk, or if this file is corrupted,
then the server will mark the index as Faulty, indicating that something is wrong with this index data files. -
If the issue with the index's data file is resolved, you can click 'Open Index' (label '3' in above figure),
so that the index is processed again. -
A possible solution is to reset the index - restart the indexing process from scratch,
so that new data files for the index are created, replacing the corrupted ones.
Note: The detailed errors list can be found in the Index Errors view.
Indexes List View - Side by Side Indexing
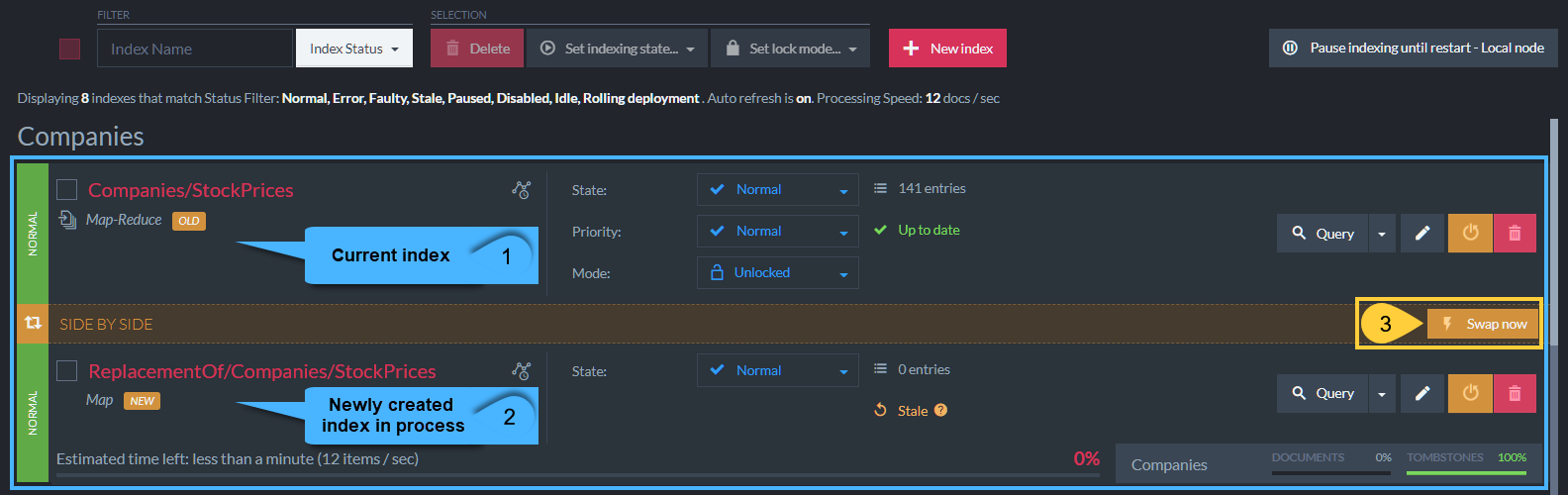
Figure-4: Indexes List View - Side by Side Indexing
-
All index updates in RavenDB are done using the side-by-side strategy.
-
When an index-definition is modified, RavenDB creates a 'new index' with the new definition.
This index will start processing all relevant documents. -
The 'old index' (label '1' in above figure) will answer queries and index new documents until
the 'new index' (label '2' in above figure) is caught up and has indexed everything. -
Once the 'new index' has completed its work, it will automatically replace the old one.
You can also force an immediate replacement if needed, by clicking 'Swap Now' (label '3' in above figure). -
The 'old index' definition can still be referenced as RavenDB keeps history of index revisions, allowing you to revert an index to any of its past revisions.
Indexes List View - Rolling Deployment
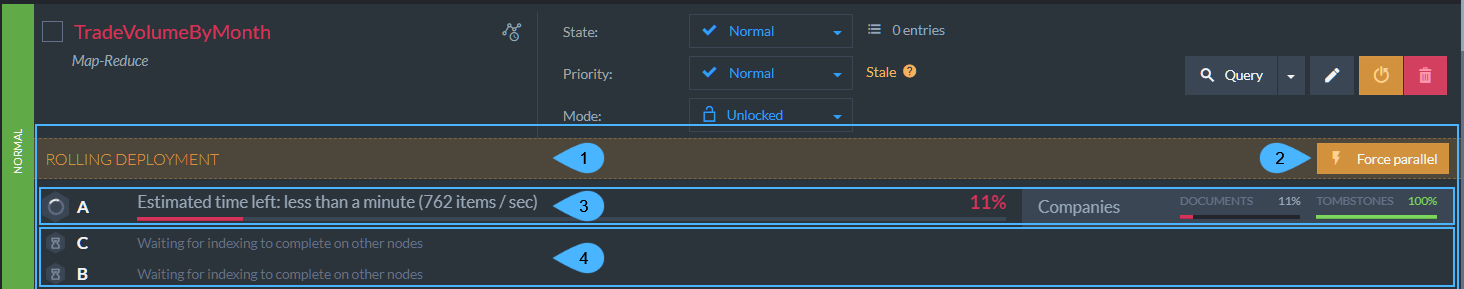
Figure-5: Indexes List View - Rolling Deployment
1. Rolling Deployment
- When an index that is defined with Rolling Deployment is created or modified, the indexing process progress is displayed per node.
2. Force Parallel
- Click to force parallel indexing deployment for the current node.
- The other nodes will continue deployment with the rolling mode.
3. Indexing in Progress
- Node
Ais currently running the 'TradeVolumeByMonth' index. - The indexing progress and the estimated time left are displayed.
- Read here about the rolling procedure.
4. Indexing Done
- Nodes
BandCare waiting for their turn to run the 'TradeVolumeByMonth' index. - Read here about the order of deployment.