Authentication: Manual Certificate Configuration
This article explains how to set up authentication manually by storing your certificate locally, externally or with logic you create that is foreign to RavenDB.
Please also take a look at the automated Setup Wizard which lets you set up authentication in a much easier and faster way with automatic certificate renewals.
- The Setup Wizard can process certificates that you provide
- Or the Wizard can give you a free, highly secure certificate via Let's Encrypt.
- We've developed default automatic renewals of certificates when setting up with the Setup Wizard together with Let's Encrypt.
If you choose manual setup and/or to provide your own certificate, you are responsible for its periodic renewal.
Prerequisites
To enable authentication, either Security.Certificate.Path or Security.Certificate.Load.Exec must be set in settings.json.
Please note that Security.Certificate.Load.Exec has replaced the old Security.Certificate.Exec as of 4.2 - see FAQ.
Setting up Client Certificates
When the server is manually set up with a server certificate for the first time, there are no client certificates registered in the server yet.
The first action an administrator will do is to generate/register a new client certificate.
Find detailed instructions of the process below.
You can set up various client certificates with different security clearance levels and database permissions. See Certificate Management for more about permissions.
Standard Manual Setup With Certificate Stored Locally
Certificate Requirements
RavenDB will accept .pfx server certificates that contain the private key, are not expired,
and include a basic (Key Usage) field and an enhanced (Enhanced Key Usage) field.
-
Key Usage
Permissions granted by this field: Digital Signature, Key Encipherment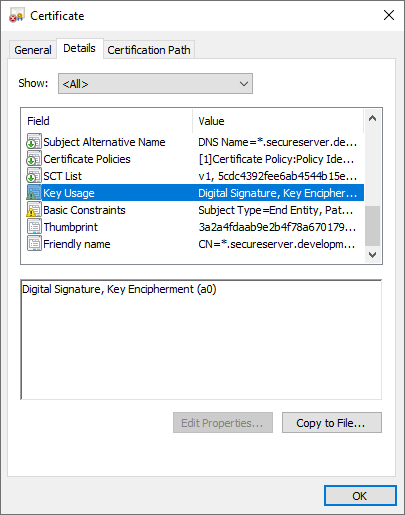
Key Usage
-
Enhanced Key Usage
Permissions granted by this field: Server Authentication, Client AuthenticationAn
Enhanced Key Usagefield must include these two OIDs:
1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 - Server Authentication
1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2 - Client Authentication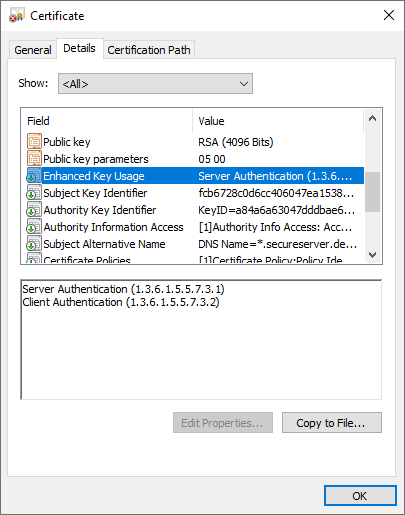
Enhanced Key Usage
- Certificates created during setup using Let's Encrypt are already provided with the above fields and OIDs.
- User-created certificates must be provided with these properties for RavenDB to accept and be able to use them.
Certificate Location
A settings.json file must reside in each node's Server folder
and define the server and certificate settings. The server will retrieve this file and use its settings on startup.
Read more about RavenDB configuration options here.
-
ServerUrl
When setting up securely, you must also set theServerUrlconfiguration option to an HTTPS address.
In manual setup, we recommend configuring a permanent port instead of a random one. In the example below, the port is set to 8080. For a list of IPs and ports already in use on your machine, runnetstat -ain the command line. -
Setup.Mode
Set to "None" if you want a manual setup. If you want to use the Setup Wizard, set to "Initial" or simply run therun.ps1file in your server package via PowerShell. -
DataDir
Configure the directory on each machine where the databases will be located. -
Path to Certificate
The standard way to enable authentication is to setSecurity.Certificate.Pathin the settings.json file with the path to your.pfxserver certificate.
You may also supply a certificate password usingSecurity.Certificate.Password, but this is optional.
For example, this is a typical settings.json for a manual setup:
{
"ServerUrl": "https://rvn-srv-1:8080",
"Setup.Mode": "None",
"DataDir": "/home/RavenData",
"Security.Certificate": {
"Path": "/home/secrets/server.pfx",
"Password": "s3cr7t p@$$w0rd"
}
}
With Logic Foreign to RavenDB or External Certificate Storage
The second way to enable authentication is to set Security.Certificate.Load.Exec.
This option is useful when you want to protect your certificate (private key) with other solutions such as "Azure Key Vault", "HashiCorp Vault"
or even Hardware-Based Protection. RavenDB will invoke a process you specify, so you can write your own scripts / mini-programs and
apply the logic that you need.
This creates a clean separation between RavenDB and the secret store in use.
RavenDB expects to get the raw binary representation (byte array) of the .pfx certificate through the standard output.
Let's look at an example -
To use Security.Certificate.Load.Exec with a PowerShell script, the settings.json
must be stored in each node's Server folder and will look something like this:
{
"ServerUrl": "https://rvn-srv-1:8080",
"Setup.Mode": "None",
"DataDir": "RavenData",
"Security.Certificate.Load.Exec": "powershell",
"Security.Certificate.Load.Exec.Arguments": "C:\\secrets\\give_me_cert.ps1 90F4BC16CA5E5CB535A6CD8DD78CBD3E88FC6FEA"
}A sample powershell script called give_me_cert.ps1 that matches the settings.json configuration:
try
{
$thumbprint = $args[0]
$cert = gci "cert:\CurrentUser\my\$thumbprint"
$exportedCertBinary = $cert.Export("Pfx")
$stdout = [System.Console]::OpenStandardOutput()
$stdout.Write($exportedCertBinary, 0, $exportedCertBinary.Length)
}
catch
{
write-error $_.Exception
exit 3
}Note
In all secure configurations, the ServerUrl must contain the same domain name that is used in the certificate (under the CN or ASN properties).
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Certificate
-
Set up file infrastructure and download server.
- Create a user account. You should get an email with your license key.
- Download the RavenDB...zip server package.
- Extract the .zip into the folders on each machine where the server nodes will permanently live.
- Store server certificate in your desired location with secure permissions.
-
In each node
Serverfolder, create thesettings.jsonfile which you will configure like the examples above.- You can do this by going into the node
Serverfolder > right-click > New > Text Document > name itsettings.jsoninstead of ...txt > click Yes > open it and begin configuring. - Place the
settings.jsoninside each node'sServerfolder because when you run the server, RavenDB is programmed to find the settings there.
- You can do this by going into the node
-
Configure the
settings.jsonfile in each nodeServerfolder.- Set the
ServerUrl. Make sure to usehttpsand that it matches the domain established in your certificate. - Set
Setup.ModetoNoneto deactivate the RavenDB Setup Wizard. - Set
DataDirto the desired database storage folder on each machine. - Set the
Security.Certificate.Pathto the .pfx that you placed in each server folder if certificate is stored with RavenDB logic on local machines orSecurity.Certificate.Load.Execif using external location or logic. -
Make sure that the certificate .path or .load script lead to the correct certificate location.
.Pathshould look something like this:
"Security.Certificate.Path": "C:/Windows/MyDomainName/A/Server/ravendb.domain.com.pfx"
See .json example for a .Path situation above. - Setting a password on the certificate is optional. See settings.json example above.
Run
- Set the
-
Right-click and run the
run.ps1(orrun.shin Linux) in the extracted server package. In Windows, it runs in PowerShell as a default.- If you don't yet have a client certificate installed, it will start up and launch a browser window that should give an error message about a missing client certificate. Setting up the client certificate is the next two steps.
-
If there is a previously existing client certificate on the machine, the browser will ask which certificate to use.
Until you set up the correct client certificate for this server (in the next two steps), it probably won't work and will give an error message.
This is because your browser will likely save your choice in the cache if you aren't in 'incognito' mode.
- It's best to first do the next two steps before selecting a client certificate in your browser.
-
The PowerShell CLI window will be running the server terminal. The last line should read
ravendb>. In the CLI, run the generateClientCert command to generate a client certificate.- The following is a generic RavenDB CLI command.
ravendb> generateClientCert <your-client-certificate-name> <path-to-output-folder> <number of months> [optional password] - In the following example the certificate will be named RavenDBClient, will be stored at C:\Users\administrator\Documents, will be valid for 60 months, and will have no password.
If a password is required add it to the end of the command.
ravendb> generateClientCert RavenDBClient C:\Users\administrator\Documents 60 - A few seconds after running this command, a
.zipfile will download into the output folder that you defined.
- The following is a generic RavenDB CLI command.
-
Extract the contents of the .zip file generated into the folders where your nodes live.
-
Install the client certificate into the OS by double-clicking the
admin.client.certificate...pfxfile and complete the OS Certificate Import Wizard.- To install the client certificate without a password, you can use the default settings by pressing Next all the way through. In most cases, this is sufficient.
- To set a password on the client certificate, do so in the Import Wizard. You'll need to use that password every time you work with the certificate.
Set client certificate password
-
Install the client certificate into the OS by double-clicking the
-
Quit and restart the server with the
run.ps1script. Select the certificate in the popup and click "OK". The RavenDB Studio should now open.- In the PowerShell window type quit to close down the server for the next important step of setting it up as an OS service.
-
To set up as an OS service, run PowerShell as an administrator and navigate to the root
Serverfolder where thesettings.jsonis located.
Copy and paste the following command.\rvn.exe windows-service register --service-name RavenDB.It will set up the cluster as an OS service, which will launch the server automatically every time the machine starts, but will fail to start if the Local Service account doesn't have access to all the required resources.
- Open the "Services" manager for Windows. Make sure that the "RavenDB" service is there and that the Startup Type is "Automatic".
-
Now the service should run whenever the machine starts and the Studio should be accessible by the user with the client certificate.
- See Certificate Management for an easy way to generate various client certificates with customizable permissions.