Cluster Transaction - Atomic Guards
-
Atomic Guards are compare exchange key/value items that RavenDB creates and manages automatically to guarantee ACID transactions in cluster-wide sessions.
Each document will be associated with its own unique atomic guard item. -
Atomic guards coordinate work between sessions that try to write on a document at the same time.
Saving a document is prevented if another session has incremented the atomic guard Raft index, which is triggered by changing the document. -
Prior to the introduction of this feature (in RavenDB 5.2), client code had to administer compare-exchange entries explicitly. You can still do that if you wish by disabling the automatic usage of atomic guards in a session and defining and managing compare exchange key/value pairs yourself where needed.
We strongly recommend not to manage atomic guards manually since doing so could cancel RavenDB's ACID transaction guarantees. Read more about this here.
-
In this page:
How Atomic Guards Work
Atomic guards are created and managed by default only when the session's transaction mode is set to ClusterWide. The atomic guards are managed as follows:
-
New document:
A new atomic guard is created when successfully saving a new document. -
Existing document that doesn't have an atomic guard:
A new atomic guard is created when modifying an existing document that does not yet have an associated atomic guard. -
Existing document that already has an atomic guard:
-
Whenever one session modifies a document that already has an associated atomic guard,
the value of its related atomic guard increases.
This allows RavenDB to detect that changes were made to this document. -
If other sessions have loaded the document before the version changed,
they will not be able to modify it if trying to save after the first session already saved it,
and aConcurrencyExceptionwill be thrown. -
If the session
saveChanges()fails, the entire session is rolled-back and the atomic guard is not created.
Be sure that your business logic is written so that if a concurrency exception is thrown, your code will re-execute the entire session.
-
Atomic Guard Transaction Scope
-
Atomic guards are local to the database they were defined on.
-
Since atomic guards are implemented as compare-exchange items,
they are Not externally replicated to another database by any ongoing replication task.
Learn more in why compare-exhange items are not replicated.
Syntax and Usage
In the code sample below, an atomic guard is automatically created upon the creation of a new document,
and then used when two sessions compete on changing the document.
const user = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe"
};
// Open a cluster-wide session
const session = documentStore.openSession({
transactionMode: "ClusterWide"
});
await session.store(user, "users/johndoe");
await session.saveChanges();
// An atomic-guard is now automatically created for the new document "users/johndoe".
// Open two more cluster-wide sessions
const session1 = documentStore.openSession({
transactionMode: "ClusterWide"
});
const session2 = documentStore.openSession({
transactionMode: "ClusterWide"
});
// The two sessions will load the same document at the same time
const loadedUser1 = await session1.load("users/johndoe");
loadedUser1.name = "jindoe";
const loadedUser2 = await session2.load("users/johndoe");
loadedUser2.name = "jandoe";
// session1 will save changes first, which triggers a change in the
// version number of the associated atomic-guard.
await session1.saveChanges();
// session2.saveChanges() will be rejected with a ClusterTransactionConcurrencyException
// since session1 already changed the atomic-guard version,
// and session2 saveChanges uses the document version that it had when it loaded the document.
await session2.saveChanges(); After running the above example, the atomic guard that was automatically created can be viewed in the Studio,
in the Compare-Exchange view:
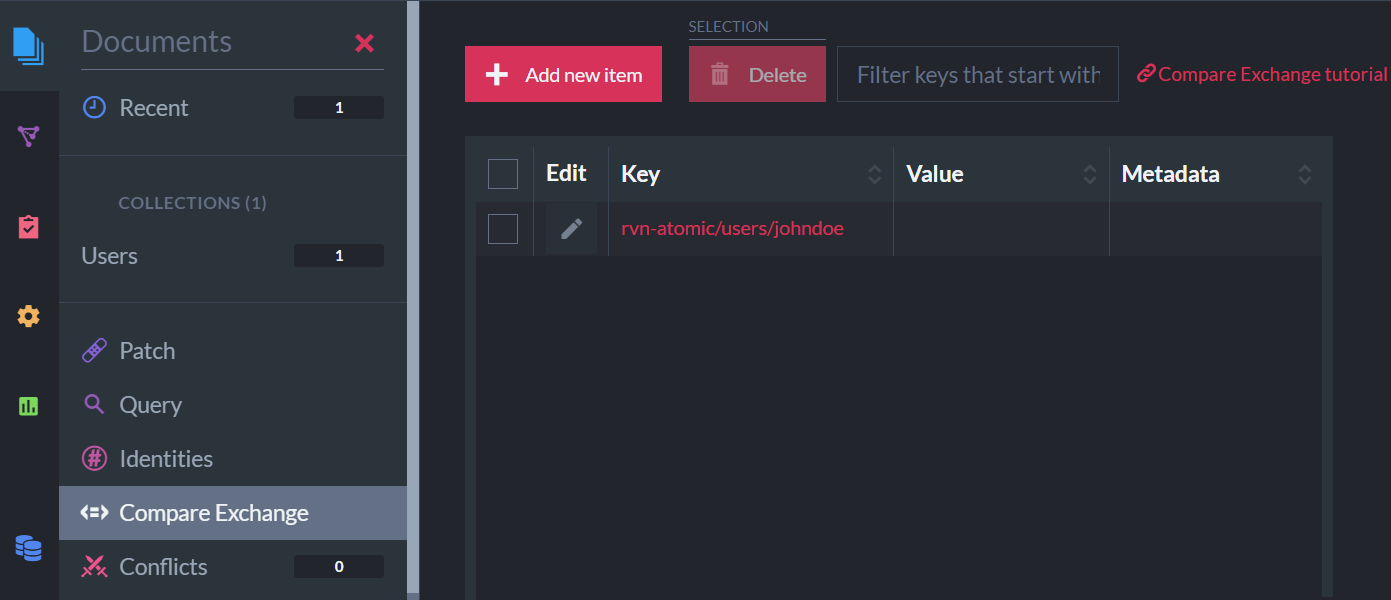
Atomic Guard
The generated atomic guard key name is composed of:
- The prefix
rvn-atomic - The ID of the document that it is associated with
Disabling Atomic Guards
To disable the automatic creation & usage of atomic guards in a session, set the session
disableAtomicDocumentWritesInClusterWideTransaction configuration option to true.
In the sample below, the session uses no atomic guards.
// Open a cluster-wide session
const session = documentStore.openSession({
transactionMode: "ClusterWide",
// Disable atomic-guards
disableAtomicDocumentWritesInClusterWideTransaction: true
});
await session.store(user, "users/johndoe");
// No atomic-guard will be created upon saveChanges
await session.saveChanges();Warning
-
To enable ACIDity in cluster-wide transactions when atomic guards are disabled,
you have to explicitly set and use the required compare exchange key/value pairs. -
Only disable and edit atomic guards if you truly know what you're doing as it can negatively impact ACID transaction guarantees.
-
Do not remove or edit atomic guards manually while a session is using them.
A session that is currently using these removed atomic guards will not be able to save their related documents resulting in an error.- If you accidentally remove an active atomic guard that is associated with an existing document,
recreate or save the document again in a cluster-wide session which will re-create the atomic guard.
- If you accidentally remove an active atomic guard that is associated with an existing document,
recreate or save the document again in a cluster-wide session which will re-create the atomic guard.
When are Atomic Guards Removed
Atomic guards expire on the expiration of the documents they are used for and are automatically removed by a RavenDB cleanup task. You do not need to handle the cleanup yourself.
Since different cleanup tasks handle the removal of deleted and expired documents and the removal of expired atomic guards, it may happen that atomic guards of removed documents would linger in the compare exchange entries list a short while longer before they are removed.
- You do not need to remove such atomic guards yourself, they will be removed by the cleanup task.
- You can re-create expired documents whose atomic guards haven't been removed yet.
RavenDB will create new atomic guards for such documents, and expire the old ones.