Knowledge Base: Numbers in RavenDB
-
Rational numbers are infinitely big and infinitely small, in computer science we are able to "model" the universe with a limited degree of accuracy and range. RavenDB is not an exception and has it's own boundaries of accuracy and range, which match most common cases of any business application.
-
This article is planned for users who know that they are going to use uncommon numeric ranges.
It will cover the way RavenDB's Server approaches numeric values and what level of range and accuracy can be expected from each of it's mechanisms. -
RavenDB's Client support of numbers depends on platform and chosen deserialization.
In this page:
About numbers
Although real numbers have no limits in size or precision, in computing there are limitations.
Simplest type of numbers known to computers are integers. RavenDB fully supports integers of int type between [-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647].
Simplest type of fraction known to computers are floating point numbers. RavenDB fully supports double precision floating point number with approximate range of 15-16 digits between [±5.0 × 10^(−324) to ±1.7 × 10^308].
RavenDB supports storing numbers in the range of the double type described above. RavenDB supports storing number in any precision, but it's indexing and JavaScript mechanisms are limited to the 16 digits precision of double numbers.
In order to better understand the terms precision and range, please observe the next diagram, comparing range and precision of 3 common .NET types: long, double and decimal:
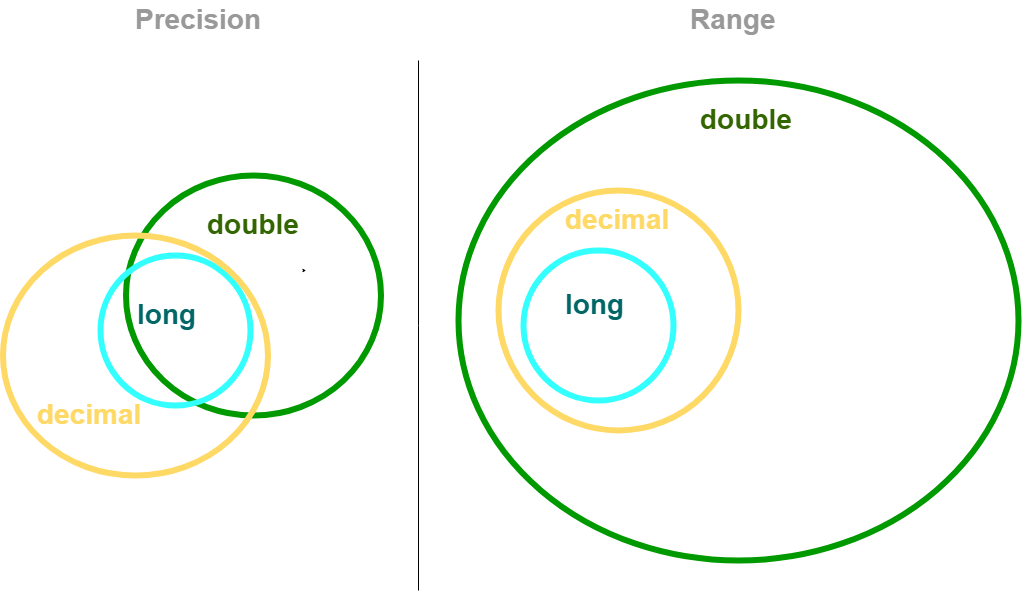
Numbers bigger then double precision max number will be rejected by server. Mechanisms supporting only double precision numbers will by default truncate the number to a double, loosing precision.
Please follow the next paragraphs to learn more about those limitations and possible workarounds.
Important edge cases
Please note that long's max and min numbers are beyond the accuracy range of double, therefore, it should be used with care, and it's recommended to avoid using it for global maximum or minimum notations.
Examples in the page
Examples in this page are based on the InterstellarTrip entity, describing an intergalactic journey of a brave pioneer:
public class InterstellarTrip
{
public class Segment
{
public string SourcePlanet { get; set; }
public string DestinationPlanet { get; set; }
public decimal DistanceInKilometers { get; set; }
}
public string TripName { get; set; }
public List<Segment> TripTrack { get; set; }
public decimal TotalDistance { get; set; }
public decimal GasBill { get; set; }
}Numbers in documents
Numbers in documents represented by either:
longfor integers in thelongrange (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807)LazyNumberValuefor all the other numbers, including other integers and floating point numbers.LazyNumberValueWraps a string representation of a number.
RavenDB server will accept document with numbers in the range of 'double' with any precision.
Numbers in JavaScript engine
RavenDB uses JavaScript in many mechanisms: projections in queries, subscriptions, ETL processes and more.
The only type of numbers supported by JavaScript is double precision floating point number, and Jint, the JavaScript engine RavenDB uses is no exception.
precision of any number that is outside of the precision range of double will be truncated to the digits amount of a double.
RavenDB provides a way to receive the original value, before the cast to double. The only limitation is that it won't be possible to treat it as a number, but you will be able to receive a string representation of the value.
The way to do that is using the scalarToRawString extension method, example:
From InterstellarTrips as trip
Where trip.Name = $name
Select {
Name:a.Name,
TotalDistance: scalarToRawString(a, x=> x.TotalDistance)
GasBill: scalarToRawString(a, x=> x.GasBill)
}
Numbers in indexes and queries
RavenDB's indexes supports either integers in the long range, or fractions in the double range.
Integers outside of the long boundaries will be treated as double and therefore their precision will be truncated to double's.
Because of that, those truncated numbers indexed value won't be equal to the original value, therefore, queries may not return the expected results.
In order to overcome that, it is recommended to treat those values as strings. The implication is that it will be possible to perform only string related queries and not numeric ones.
Static indexes
The way to treat numbers that exceed the precision level of long or double in static indexes, the string representation of the value should be indexed, It will use the raw value, rather the truncated one.
Map = interstellarTrips => from trip in interstellarTrips
select new
{
TotalDistance = trip.TotalDistance.ToString()
};Query
Query work as expected with integers in the 'long' range and fractions in the double range and precision.
In order to query numbers outside of that range, query the the field using the string representation of the value, whether if using an index or a collection query.
From InterstellarTrips as trip
Where trip.Name = $name
Select {
Name:a.Name,
TotalDistance: scalarToRawString(a, x=> x.TotalDistance)
GasBill: scalarToRawString(a, x=> x.GasBill)
}Note that alphanumeric sorting of string representation of numbers is accurate only with integers. Alphanumeric sorting of fractions and numbers with exponent notations will not analyze the value as a number.
Numbers in management studio
The management studio treats documents as JavaScript objects, therefore, it treats it's numbers as a JavaScript number, which is always a double.
Note that editing documents with numeric data outside of the precision range of double will end up with truncating those numbers to a proper double and unintentional modification of those fields.
Numbers in client API
Numbers in RavenDB clients depend on the limitations of the platforms and the serialization/deserialization mechanisms. See articles in the desired languages: