Polymorphic indexes
By default, RavenDB indexes operate only on a specific entity type, or a Collection, and it ignores the inheritance hierarchy when it does so.
For example, let us assume that we have the following inheritance hierarchy:
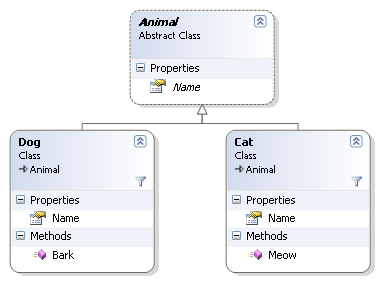
If we saved a Cat, it would have an Entity-Name of "Cats" and if we saved a Dog, it would have an Entity-Name of "Dogs".
If we wanted to index cats by name, we would write:
from cat in docs.Cats
select new { cat.Name }And for dogs:
from dog in docs.Dogs
select new { dog.Name }This works, but each index would only give us results for the animal it has been defined on. But what if we wanted to query across all animals?
Multi-map indexes
The easiest way to do this is by writing a multi-map index like this one:
public class AnimalsIndex : AbstractMultiMapIndexCreationTask
{
public AnimalsIndex()
{
AddMap<Cat>(cats => from c in cats
select new { c.Name });
AddMap<Dog>(dogs => from d in dogs
select new { d.Name });
}
}And query it like this:
var results = session.Advanced.LuceneQuery<object>("AnimalsIndex").WhereEquals("Name", "Mitzy");You can also use the Linq provider if your objects implement an interface, IAnimal for instance:
session.Query<IAnimal>("AnimalsIndex").Where(x => x.Name == "Mitzy");Other ways
Another option would be to modify the way we generate the Entity-Name for subclasses of Animal, like so:
var documentStore = new DocumentStore()
{
Conventions =
{
FindTypeTagName = type =>
{
if (typeof(WhereEntityIs.Animal).IsAssignableFrom(type))
return "Animals";
return DocumentConvention.DefaultTypeTagName(type);
}
}
};Using this method, we can now index on all animals using:
from animal in docs.Animals
select new { animal.Name }But what happen when you don't want to modify the entity name of an entity?
You can create a polymorphic index using:
from animal in docs.WhereEntityIs("Cats", "Dogs")
select new { animal.Name }That would generate an index that would match both Cats and Dogs.