Bundle: SQL Replication: Basics
To provide an easy and flexible way to setup a replication to SQL servers, we have replaced the Index Replication bundle with new mechanism that is a part of a SQL Replication bundle.
Supported SQL providers:
* System.Data.SqlClient
* System.Data.SqlServerCe.4.0
* System.Data.SqlServerCe.3.5
* System.Data.OleDb
* System.Data.OracleClient
* MySql.Data.MySqlClient
* Npgsql
Setup
To configure SQL Replication, we need to enable the SQL Replication Bundle and insert a SQL Replication Configuration document into our database. This can be done by using the Studio or manually by inserting proper document (Raven.Database.Bundles.SqlReplication.SqlReplicationConfig) under Raven/SqlReplication/Configuration/name_here key.
The document format is as follows:
public class SqlReplicationConfig
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool Disabled { get; set; }
public bool ParameterizeDeletesDisabled { get; set; }
public bool ForceSqlServerQueryRecompile { get; set; }
public bool QuoteTables { get; set; }
public string RavenEntityName { get; set; }
public string Script { get; set; }
public string FactoryName { get; set; }
public string ConnectionString { get; set; }
public string PredefinedConnectionStringSettingName { get; set; }
public string ConnectionStringName { get; set; }
public string ConnectionStringSettingName { get; set; }
public List<SqlReplicationTable> SqlReplicationTables { get; set; }
}
public class SqlReplicationTable
{
public string TableName { get; set; }
public string DocumentKeyColumn { get; set; }
public bool InsertOnlyMode { get; set; }
}where:
| Id | document identifier |
| Name | configuration name |
| Disabled | marks replication as enabled/disabled |
| ParameterizeDeletesDisabled | disabled the parameterization of deletes |
| ForceSqlServerQueryRecompile | forces statement recompilation on SQL Server |
| QuoteTables | toggles table name quotation |
| RavenEntityName | name of entities (collection) that will be replicated |
| Script | replication script |
| FactoryName ConnectionString ConnectionStringName ConnectionStringSettingName PredefinedConnectionStringSettingName |
used to provide connection strings to destination DB in various ways |
| SqlReplicationTables | list of tables to which the documents will be replicated, with the ability to turn on append only mode (InsertOnlyMode), which will skip any deletions, increasing performance |
Example
Let us consider a simple scenario, where we have an Order with OrderLines (from Northwind) and we want to setup a replication to MSSQL.
public class Order
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Company { get; set; }
public string Employee { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderedAt { get; set; }
public DateTime RequireAt { get; set; }
public DateTime? ShippedAt { get; set; }
public Address ShipTo { get; set; }
public string ShipVia { get; set; }
public decimal Freight { get; set; }
public List<OrderLine> Lines { get; set; }
}
public class OrderLine
{
public string Product { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
public decimal PricePerUnit { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
public decimal Discount { get; set; }
}
public class Address
{
public string Line1 { get; set; }
public string Line2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public string PostalCode { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
}First we need to setup our MSSQL by creating a database with two tables. In our case the database will be called ExampleDB and the tables will be called Orders and OrderLines.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[OrderLines]
(
[Id] int identity primary key,
[OrderId] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[Qty] [int] NOT NULL,
[Product] [nvarchar] (255) NOT NULL,
[Cost] [decimal] (18,2) NOT NULL
)
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Orders]
(
[Id] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[OrderLinesCount] [int] NOT NULL,
[TotalCost] [decimal] (18,2) NOT NULL
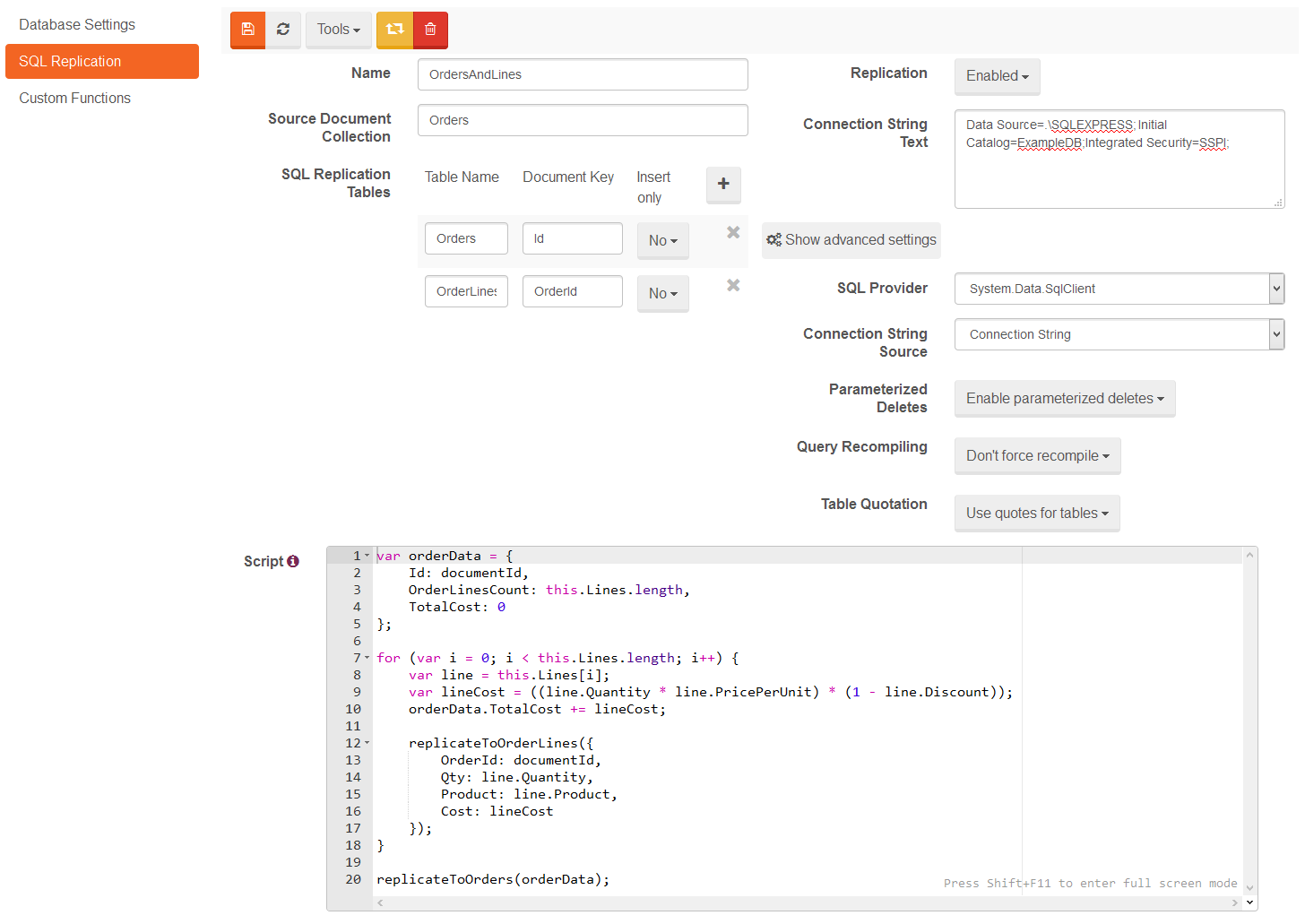
)Last step is to insert a document with our configuration. This can be done using Studio or manually.
Manual
session.Store(new SqlReplicationConfig
{
Id = "Raven/SqlReplication/Configuration/OrdersAndLines",
Name = "OrdersAndLines",
ConnectionString = @"
Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;
Initial Catalog=ExampleDB;
Integrated Security=SSPI;",
FactoryName = @"System.Data.SqlClient",
RavenEntityName = "Orders",
SqlReplicationTables =
{
new SqlReplicationTable
{
TableName = "Orders", DocumentKeyColumn = "Id"
},
new SqlReplicationTable
{
TableName = "OrderLines", DocumentKeyColumn = "OrderId"
},
},
Script = @"
var orderData = {
Id: documentId,
OrderLinesCount: this.Lines.length,
TotalCost: 0
};
for (var i = 0; i < this.Lines.length; i++) {
var line = this.Lines[i];
var lineCost = ((line.Quantity * line.PricePerUnit) * (1 - line.Discount));
orderData.TotalCost += lineCost;
replicateToOrderLines({
OrderId: documentId,
Qty: line.Quantity,
Product: line.Product,
Cost: lineCost
});
}
replicateToOrders(orderData);"
});Using Studio
In Studio the configuration page is found under Settings -> SQL Replication.
Custom functions in Script
In Script beside built-in functions, custom ones can be introduced. Please visit this page if you want to know how to add custom functions.
There also also two additional functions created specifically for SQL Replication:
varchar(value, size = 50) |
method | Defines parameter type as varchar with ability to specify its size (50 if not specified). |
nVarchar(value, size = 50) |
method | Defines parameter type as nvarchar with ability to specify its size (50 if not specified). |
Remarks
Information
The script will be called once for each document in the source document collection, with this representing the document, and the document id available as documentId. Call replicateTo<TableName>() (e.g. replicateToOrders) for each row you want to write to the database.
Performance
For performance reasons, it is required to have a secondary (or primary) index for document key in SQL Tables (in the example above for Orders.Id and OrderLines.OrderId). Otherwise, especially at scale, performance degradation may occur.