Ongoing Tasks: SQL ETL
SQL ETL is a task that creates an ETL process for a given database where the destination is a relational database.
- In this page:
Creating a Task
Settings -> Manage Ongoing Tasks.
Supported Databases
RavenDB can ETL to the following relational databases:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle
You need to choose the provider type when defining a connection string.
Relational Database Setup
Before you start with SQL ETL you need to create tables in a relational database. Those will be the destinations for records produced by ETL scripts.
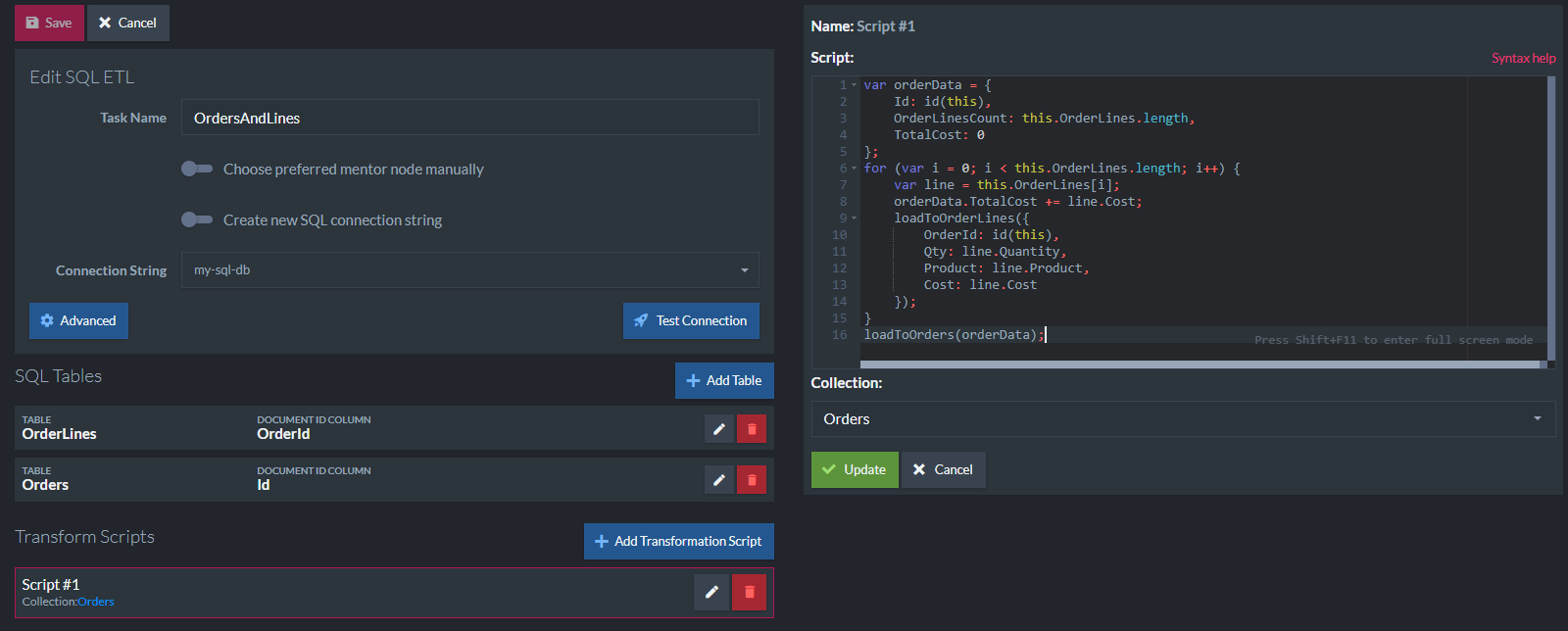
SQL Tables
The SQL ETL configuration starts from defining which tables are going to be used in the ETL process. Each table needs to have a column specified that is going to be used as the document ID column. RavenDB will put source document IDs there that will be used to handle updates and deletes of documents. The column doesn't have to be the primary key of a table.
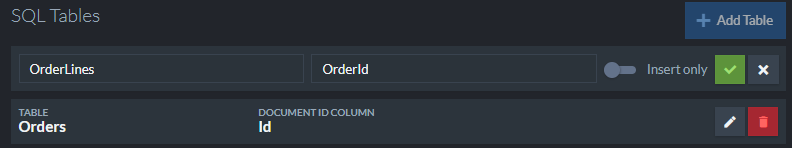
Insert only
SQL ETL process performs updates of documents via DELETE and INSERT statements issued to the relational database. If your system is append-only you can tell RavenDB to insert the data directly without running a set of DELETE statements first. It can be a nice performance boost when dealing with those kind of systems.
Indexes
Due to performance reasons you should define indexes in SQL tables on at least the column used to hold the document ID.
Transformation Scripts
A task can have multiple transformations dealing with relational tables. The script is defined per collection. It cannot be empty.
loadTo Method
The script is executed per document once it is created or modified. In order to load data to the destination table you need to call loadTo<TableName>() method and pass JS object.
It is a convention that a table name of the relational database that a document will be inserted is indicated in the load method name.
For example, if you want to write data to OrderLines table you need to call the following method in the script body:
loadToOrderLines({ ... });The method parameter must be a JS object. You can create it as follows:
loadToOrderLines({
OrderId: id(this),
Qty: line.Quantity,
Product: line.Product,
Cost: line.PricePerUnit
});Alternative Syntax
The target table name can be passed to the loadTo command separately, as a string argument,
using this syntax: loadTo('Target', obj)
- Example:
The following two calls toloadToare equivalent.
loadToEmployees(this);
loadTo('Employees', this);
- The target name
'Employees'in this syntax is not a variable and cannot be used as one: it is simply a string literal of the target's name. - Separating the target name from the
loadTocommand makes it possible to include symbols like-and.in target names. This is not possible when the standardloadToEmployeessyntax is used because including special characters in the name of a JS function turns it invalid.
Filtering
If you want to filter some documents out from the ETL you simply omit loadTo call:
if (this.ShipTo.Country === 'USA') {
// load only orders shipped to USA
loadToOrders({ ... });
}Loading Other Documents
The load method loads a document with a specified ID during script execution.
var company = load(this.Company);Accessing Metadata
You can access metadata in the following way:
var value = this['@metadata']['custom-metadata-key'];Loading to Multiple Tables
The loadTo method can be called multiple times in a single script. That allows you to split a single Order document having Lines collection into two tables and insert multiple rows:
var orderData = {
Id: id(this),
OrderLinesCount: this.Lines.length,
TotalCost: 0
};
for (var i = 0; i < this.Lines.length; i++) {
var line = this.Lines[i];
orderData.TotalCost += line.PricePerUnit * line.Quantity;
loadToOrderLines({
OrderId: id(this),
Qty: line.Quantity,
Product: line.Product,
Cost: line.PricePerUnit
});
}
orderData.TotalCost = Math.round(orderData.TotalCost * 100) / 100;
loadToOrders(orderData);Loading Attachments
You can store binary data that are kept as attachments in RavenDB using loadAttachment() method. For example, if you have the following Attachments table:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Attachments]
(
[Id] int identity primary key,
[OrderId] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
[AttachmentName] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[Data] [varbinary](max) NULL
)then you can define the script to load document's attachments:
var attachments = this['@metadata']['@attachments'];
for (var i = 0; i < attachments.length; i++) {
var attachment = {
OrderId: id(this),
AttachmentName: attachments[i].Name,
Data: loadAttachment(attachments[i].Name)
};
loadToAttachments(attachment);
}Attachments can be also accessed by using getAttachments() helper function (instead of grabbing them from metadata). The existence of an attachment can be checked by
hasAttachment(name) function.
Counters
Counters aren't supported by SQL ETL.
Transforming to VARCHAR and NVARCHAR
There also two additional functions created specifically for dealing with VARCHAR and NVARCHAR types:
varchar(value, size = 50) |
function | Defines parameter type as varchar with ability to specify its size (50 if not specified). |
nvarchar(value, size = 50) |
function | Defines parameter type as nvarchar with ability to specify its size (50 if not specified). |
var names = this.Name.split(' ');
loadToUsers(
{
FirstName: varchar(names[0], 30),
LastName: nvarchar(names[1]),
});
Transaction Processing
All records created in a single ETL run, one per each loadTo call, will be sent in a single batch and processed under the same transaction.
Advanced Options
- Command timeout - number of seconds after which SQL command will timeout. It overrides value defined in
ETL.SQL.CommandTimeoutInSecsetting. Default: null (use provider default). - Parameterized deletes - toggles the parameterization of DELETE statements
- Force recompile query - forces statement recompilation on SQL Server (
OPTION(RECOMPILE)) - Table quotation - toggles table name quotation