Page Query Results
-
Paging:
Paging is the process of fetching a subset (a page) of results from a dataset, rather than retrieving the entire results at once. This method enables processing query results one page at a time. -
Default page size:
If the client's query definition does Not explicitly specify the page size, the server will default toint.MaxValue(2,147,483,647). In such case, all results will be returned in a single server call. -
Performance:
Using paging is beneficial when handling large result datasets, contributing to improved performance.
See paging and performance here below. -
Paging policy:
To prevent executing queries that do not specify a page size, you can set the ThrowIfQueryPageSizeIsNotSet convention, which can be useful during development or testing phases. -
In this page:
No paging example
The queries below will return all the results available.
List<Product> results = session
.query(Product.class, Products_ByUnitsInStock.class)
.whereGreaterThan("UnitsInStock", 10)
.toList();public static class Products_ByUnitsInStock extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
public Products_ByUnitsInStock() {
map = "docs.Products.Select(product => new {" +
" UnitsInStock = product.UnitsInStock" +
"})";
}
}from index "Products/ByUnitsInStock"
where UnitsInStock > 10
Paging examples
Basic paging
Let's assume that our page size is 10, and we want to retrieve the 3rd page. To do this, we need to issue following query:
List<Product> results = session
.query(Product.class, Products_ByUnitsInStock.class)
.whereGreaterThan("UnitsInStock", 10)
.skip(20) // skip 2 pages worth of products
.take(10) // take up to 10 products
.toList(); // execute querypublic static class Products_ByUnitsInStock extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
public Products_ByUnitsInStock() {
map = "docs.Products.Select(product => new {" +
" UnitsInStock = product.UnitsInStock" +
"})";
}
}from index "Products/ByUnitsInStock"
where UnitsInStock > 10
limit 20, 10 // skip 20, take 10Find total results count when paging
While paging, you sometimes need to know the exact number of results returned from the query. The Client API supports this explicitly:
Reference<QueryStatistics> stats = new Reference<QueryStatistics>();
List<Product> results = session
.query(Product.class, Products_ByUnitsInStock.class)
.statistics(stats)
.whereGreaterThan("UnitsInStock", 10)
.skip(20)
.take(10)
.toList();
int totalResults = stats.value.getTotalResults();public static class Products_ByUnitsInStock extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
public Products_ByUnitsInStock() {
map = "docs.Products.Select(product => new {" +
" UnitsInStock = product.UnitsInStock" +
"})";
}
}from index "Products/ByUnitsInStock"
where UnitsInStock > 10
limit 20, 10 // skip 20, take 10While the query will return with just 10 results, totalResults will hold the total number of matching documents.
Paging and performance
Better performance:
It is recommended to explicitly set a page size when making a query that is expected to generate a significant number of results. This practice has several benefits:
- Optimizes bandwidth usage by reducing data transfer between the server and client.
- Prevents delays in response times caused by sending too much data over the network.
- Avoids high memory consumption when dealing with numerous documents.
- Ensures a more manageable user experience by not overwhelming users with massive datasets at once.
Performance hints:
-
By default, if the number of returned results exceeds 2048, the server will issue a "Page size too big" notification (visible in the Studio) with information about the query.
-
This threshold can be customized by modifying the value of the PerformanceHints.MaxNumberOfResults configuration key.
-
As suggested by the hint, you may consider using Streaming query results instead of paging.
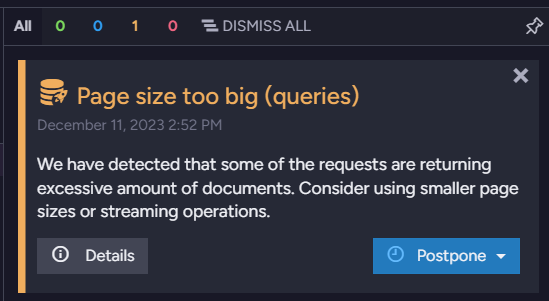
Performance Hint
Paging through tampered results
-
The
QueryStatisticsobject contains theTotalResultsproperty,
which represents the total number of matching documents found in the query results. -
The
QueryStatisticsobject also contains theSkippedResultsproperty.
Whenever this property is greater than 0, that implies the server has skipped that number of results from the index. -
The server will skip duplicate results internally in the following two scenarios:
-
When making a Projection query with Distinct.
-
When querying a Fanout index.
-
-
In those cases:
-
The
SkippedResultsproperty from the stats object will hold the count of skipped (duplicate) results. -
The
TotalResultsproperty will be invalidated -
it will Not deduct the number of skipped results from the total number of results.
-
-
In order to do proper paging in those scenarios:
include theSkippedResultsvalue when specifying the number of documents to skip for each page using:
(currentPage * pageSize) + SkippedResults. -
See the following examples:
A projection query with Distinct:
List<Product> results;
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
int skippedResults = 0;
Reference<QueryStatistics> stats = new Reference<>();
do {
results = session
.query(Product.class, Products_ByUnitsInStock.class)
.statistics(stats)
.skip((pageNumber * pageSize) + skippedResults)
.take(pageSize)
.whereGreaterThan("UnitsInStock", 10)
.distinct()
.toList();
skippedResults += stats.value.getSkippedResults();
pageNumber++;
} while (results.size() > 0);public static class Products_ByUnitsInStock extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
public Products_ByUnitsInStock() {
map = "docs.Products.Select(product => new {" +
" UnitsInStock = product.UnitsInStock" +
"})";
}
}from index "Products/ByUnitsInStock"
where UnitsInStock > 10
select distinct *
limit 0, 10 // First loop will skip 0, take 10, etc.Querying a Fanout index:
List<Order> results;
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 50;
int skippedResults = 0;
Reference<QueryStatistics> stats = new Reference<>();
do {
results = session
.query(Order.class, Order_ByOrderLines_ProductName.class)
.statistics(stats)
.skip((pageNumber * pageSize) + skippedResults)
.take(pageSize)
.toList();
skippedResults += stats.value.getSkippedResults();
pageNumber++;
} while (results.size() > 0);public static class Orders_ByOrderLines_ProductName extends AbstractIndexCreationTask {
public Orders_ByOrderLines_ProductName() {
map = "docs.Orders.SelectMany(order => order.Lines, (order, line) => new {" +
" Product = line.ProductName " +
"})";
}
}from index "Order/ByOrderLines/ProductName"
limit 0, 50 // First loop will skip 0, take 50, etc.