RavenDB ETL Task
-
A RavenDB ETL Task is an ETL process that transfers data from the current database to another RavenDB database instance, outside of the Database Group
-
The sent data can be filtered and modified by transformation scripts
-
Learn more about the benefits of using ETL in Why use ETL
-
ETL is different from data replication. See RavenDB ETL Task -vs- Replication Task
-
In RavenDB ETL, a certificate must be passed from the source server to the destination so that the destination server trusts the source.
-
In this page:
RavenDB ETL Task - Definition
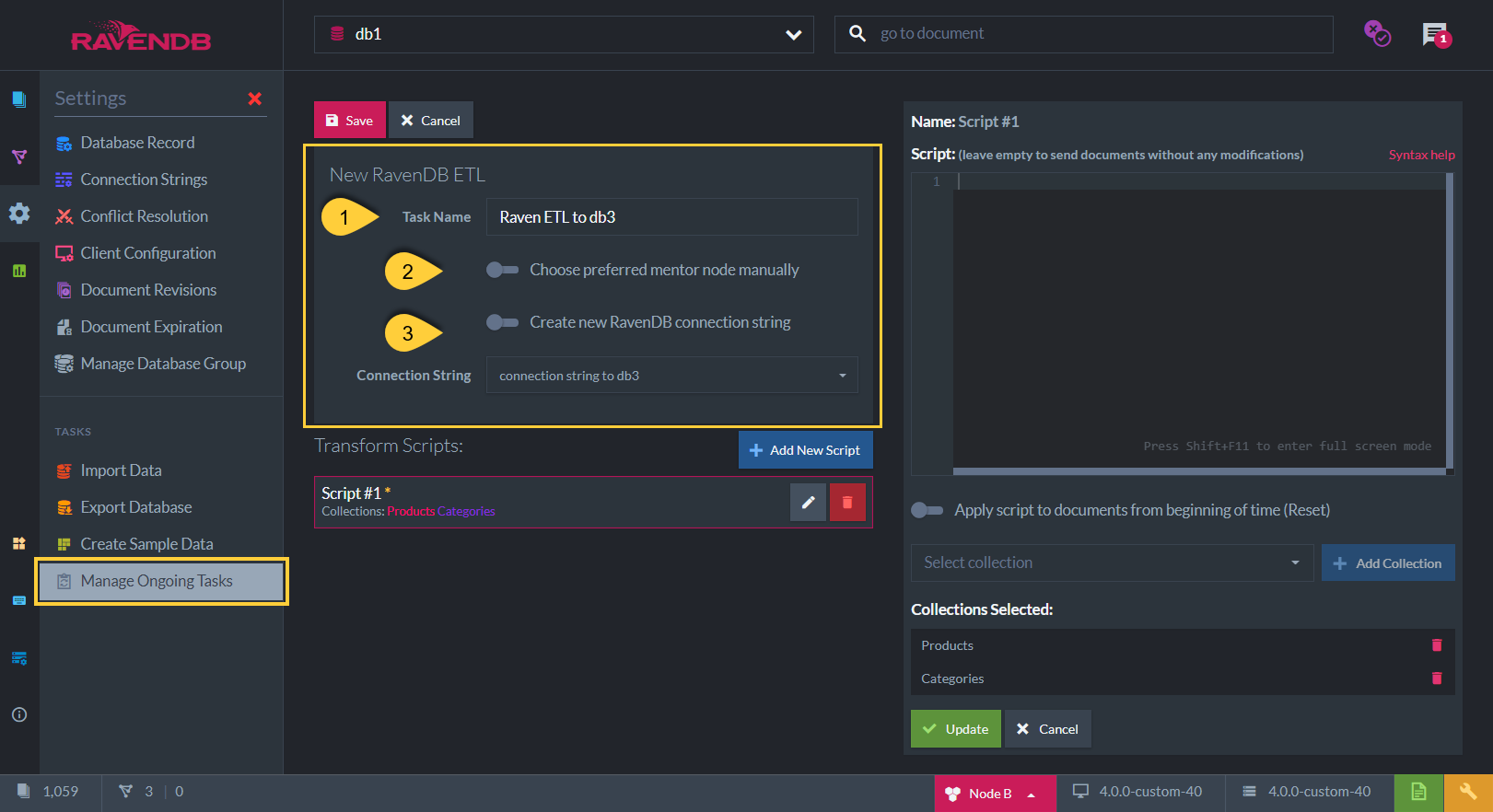
Create New RavenDB ETL Task
-
Task Name (Optional)
- Choose a name of your choice
- If no name is given then the RavenDB server will create one for you based on the defined connection string
-
Preferred Node (Optional)
- Select a preferred mentor node from the Database Group to be the responsible node for this RavenDB ETL Task
- If not selected, then the cluster will assign a responsible node (see Members Duties)
-
Connection String
- Select an existing connection string from the list or create a new one
- The connection string defines the destination database and its database group server node URLs
RavenDB ETL Task - Transform Scripts
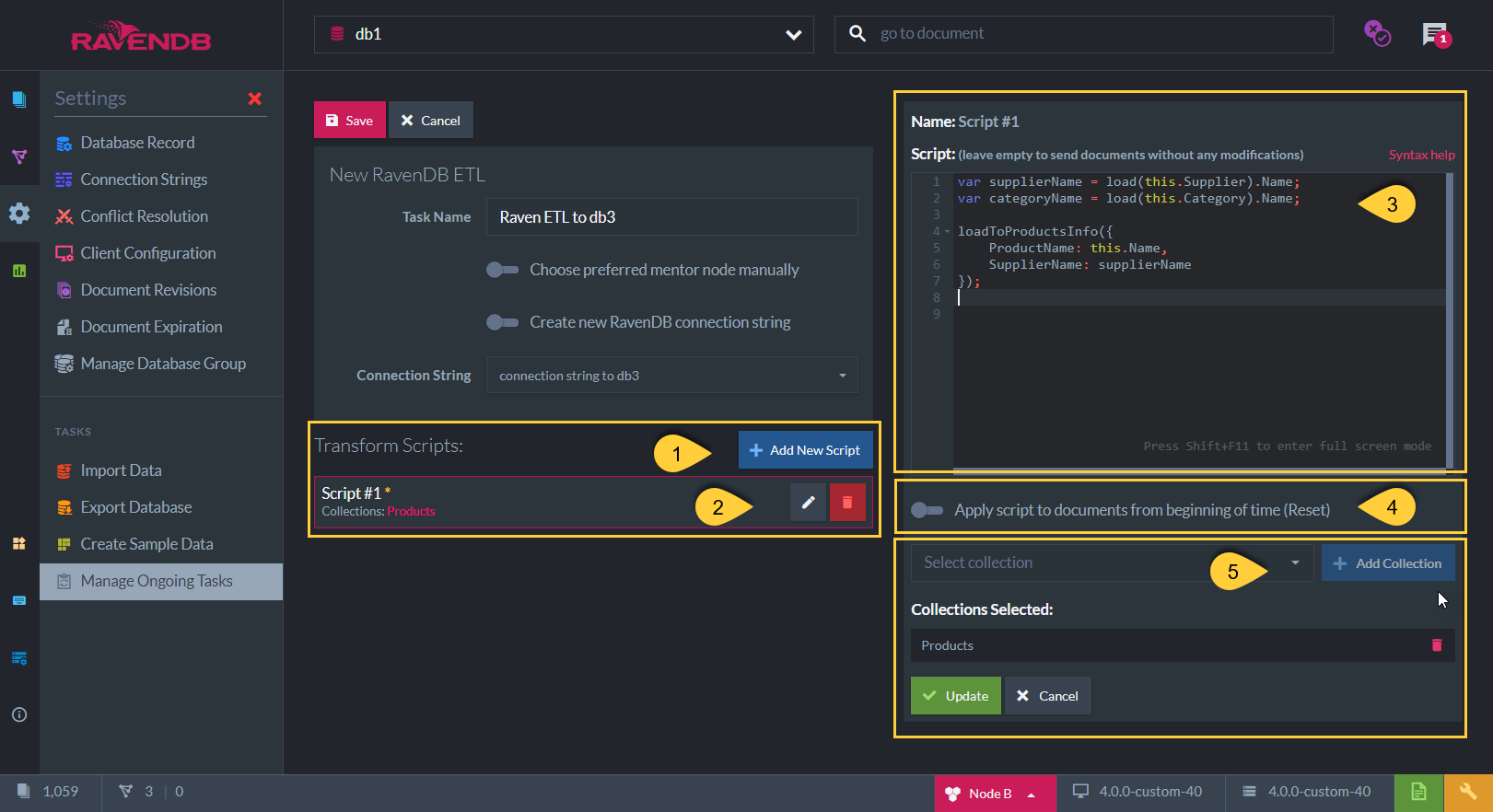
RavenDB ETL Task - Transform Scripts
-
Click to add a new script
-
Edit or Delete an existing script
-
Enter the script to use.
In the above example, each source document from the "Products" collection will be sent to the "ProductsInfo" collection in the destination database db3 (which is external to the cluster).
Each new document will have 2 fields: "ProductName" and "SupplierName".
For detailed script options see Transformation Script Options. -
By default, updates to the ETL script will not be applied to documents that were already sent.
When checking this option RavenDB will start the ETL process for this script from scratch ("beginning of time"),
rather than apply the update only to new or updated documents. -
Select the collections for the ETL task - or - apply the script to all collections
Passing Certificate Between Secure Clusters
Pass Certificate from Source Cluster to Destination Cluster
This step must be done if connecting to another cluster so that the destination cluster trusts the source.
-
Via RavenDB Studio:
Navigate from the "Manage Server" tab (left side) > "Certificates" to open the Certificate Management view.- Learn how to pass certificates here.
-
Via API:
See the code sample to learn how to define a client certificate in the DocumentStore.- To generate and configure a client certificate from the source server, see CreateClientCertificateOperation
- Learn the rationale needed to configure client certificates in The RavenDB Security Authorization Approach
RavenDB ETL Task - Details in Tasks List View
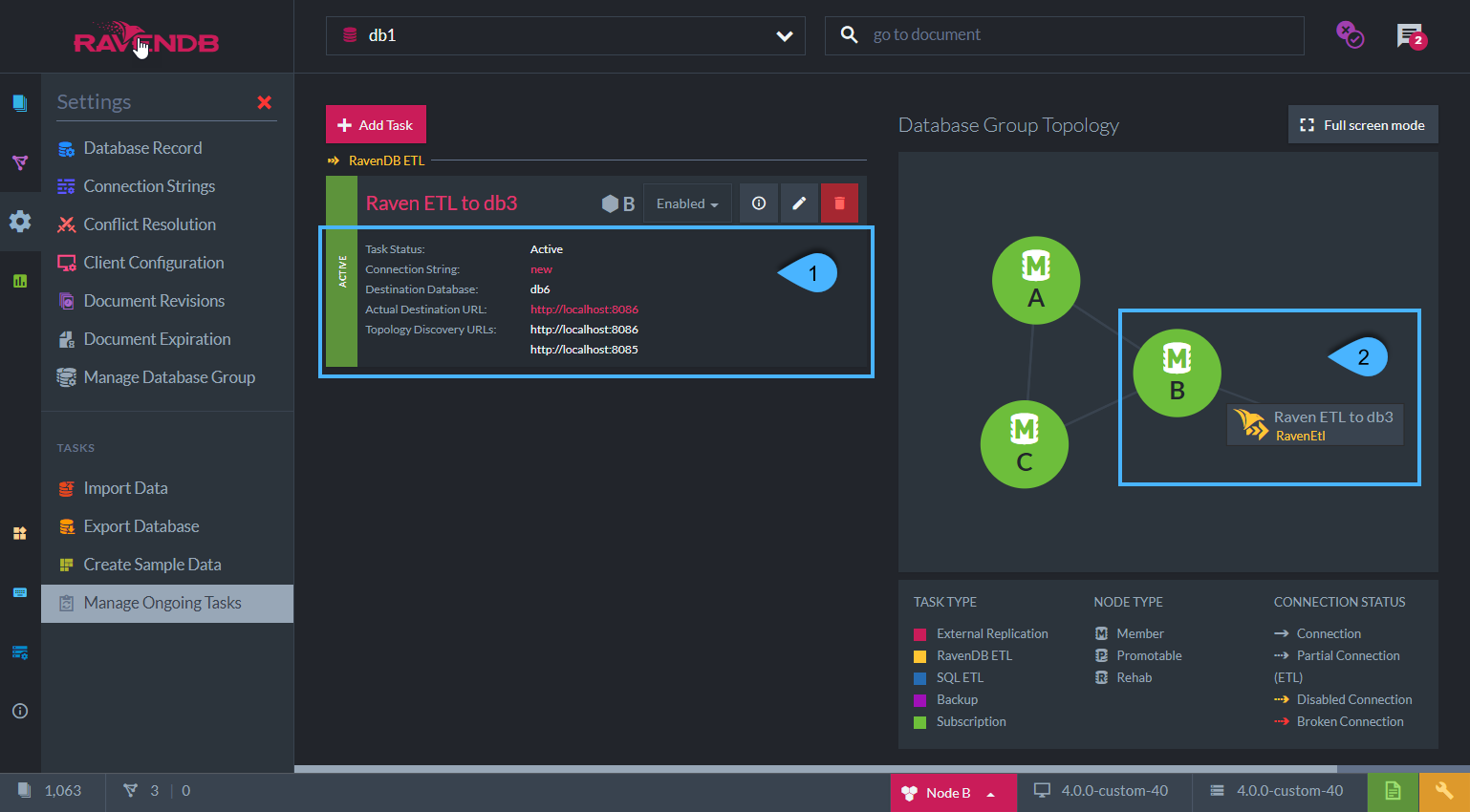
Tasks List View Details
-
RavenDB ETL Task Details:
- Task Status - Active / Not Active / Not on Node / Reconnect
- Connection String - The connection string used
- Destination Database - The destination database to which the data is being sent
- Actual Destination URL - The server URL to which the data is actually being sent,
the one that is currently used out of the available Topology Discovery URLs - Topology Discovery URLs - List of the available destination Database Group server URLs
-
Graph view:
Graph view of the responsible node for the External Replication Task
RavenDB ETL Task - Offline Behaviour
-
When the source cluster is down (and there is no leader):
-
Creating a new Ongoing Task is a Cluster-Wide operation,
thus, a new Ongoing RavenDB ETL Task cannot be scheduled. -
If a RavenDB ETL Task was already defined and active when the cluster went down,
then the task will not be active, so ETL will not take place.
-
-
When the node responsible for the ETL task is down:
- If the responsible node for the RavenDB ETL Task is down,
then another node from the Database Group will take ownership of the task so that the ETL process will continue executing.
- If the responsible node for the RavenDB ETL Task is down,
-
When the destination node is down:
-
The ETL process will wait until the destination is reachable again and proceed from where it left off.
-
If there is a cluster on the other side, and the URL addresses of the destination database group nodes are listed in the connection string, then when the destination node is down, RavenDB ETL will simply start transferring data to one of the other nodes specified.
-
RavenDB ETL Task -vs- Replication Task
-
Data ownership:
-
When a RavenDB node performs an ETL to another node it is not replicating the data, it is writing it.
In other words, we always overwrite whatever exists on the other side, there is no conflict handling. -
The source database for the ETL process is the owner of the data.
This means that as long as the destination collection is the same as the source, any modifications done to the data sent by ETL on the destination database side are lost when overwriting occurs. -
If you need to modify the data that's transferred to the destination side, you should create a companion document in the destination database instead of modifying the data sent directly.
If you modify a document that is loaded by ETL, your modifications will be lost when the ETL process deletes and loads the updated document in the destination server.
The rule is: With ETL destination documents, you can look but don't touch. -
On the other hand, data that is replicated with RavenDB's External Replication Task does not overwrite existing documents.
Conflicts are created and handled according to the destination database policy defined.
This means that you can change the replicated data on the destination database and conflicts will be solved.
-
-
Data content:
-
With the replication Task, all documents contained in the database are replicated to the destination database without any content modification.
-
Whereas in ETL, the document content sent can be filtered and modified with the supplied transformation script.
In addition, partial data can be sent as specific collections can be selected.
-