Indexes: Indexing Related Documents
-
As described in modeling considerations in RavenDB,
it is recommended for documents to be: independent, isolated, and coherent.
However, to accommodate varied models, documents can reference other documents. -
The related data from a referenced (related) document can be indexed,
this will allow querying the collection by the indexed related data. -
The related documents that are loaded in the index definition are tracked for changes.
-
In this page:
What are related documents
-
Whenever a document references another document, the referenced document is called a Related Document.
-
In the image below, document
products/34-Areferences documentscategories/1-A&suppliers/16-A,
which are considered Related Documents.
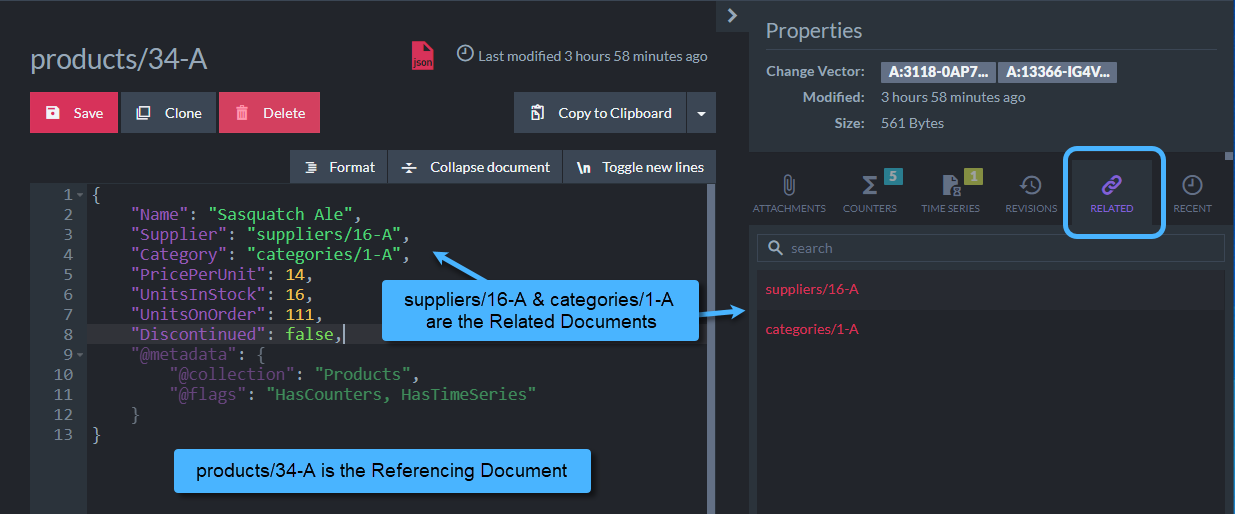
Referencing related documents
Index related documents
Example I - basic
What is tracked:
- Both the documents from the indexed collection and the indexed related documents are tracked for changes.
Re-indexing will be triggered per any change in either collection.
(See changes that cause re-indexing here).
The index:
- Following the above
Product - Categoryrelationship from the Northwind sample database,
an index defined on the Products collection can index data from the related Category document.
public class Products_ByCategoryName : AbstractIndexCreationTask<Product>
{
public class IndexEntry
{
public string CategoryName { get; set; }
}
public Products_ByCategoryName()
{
Map = products => from product in products
// Call LoadDocument to load the related Category document
// The document ID to load is specified by 'product.Category'
let category = LoadDocument<Category>(product.Category)
select new IndexEntry
{
// Index the Name field from the related Category document
CategoryName = category.Name
};
// Any change to either Products or Categories will trigger reindexing
}
}public class Products_ByCategoryName_JS : AbstractJavaScriptIndexCreationTask
{
public Products_ByCategoryName_JS()
{
Maps = new HashSet<string>()
{
// Call method 'load' to load the related Category document
// The document ID to load is specified by 'product.Category'
// The Name field from the related Category document will be indexed
@"map('products', function(product) {
let category = load(product.Category, 'Categories')
return {
CategoryName: category.Name
};
})"
// Any change to either Products or Categories will trigger reindexing
};
}
}The query:
- We can now query the index for Product documents by
CategoryName,
i.e. get all matching Products that reference a Category that has the specified name term.
IList<Product> matchingProducts = session
.Query<Products_ByCategoryName.IndexEntry, Products_ByCategoryName>()
.Where(x => x.CategoryName == "Beverages")
.OfType<Product>()
.ToList();IList<Product> matchingProducts = await asyncSession
.Query<Products_ByCategoryName.IndexEntry, Products_ByCategoryName>()
.Where(x => x.CategoryName == "Beverages")
.OfType<Product>()
.ToListAsync();from index "Products/ByCategoryName"
where CategoryName == "Beverages"Example II - list
The documents:
// The referencing document
public class Author
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
// Referencing a list of related document IDs
public List<string> BookIds { get; set; }
}
// The related document
public class Book
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}The index:
- This index will index all names of the related Book documents.
public class Authors_ByBooks : AbstractIndexCreationTask<Author>
{
public class IndexEntry
{
public IEnumerable<string> BookNames { get; set; }
}
public Authors_ByBooks()
{
Map = authors => from author in authors
select new IndexEntry
{
// For each Book ID, call LoadDocument and index the book's name
BookNames = author.BookIds.Select(x => LoadDocument<Book>(x).Name)
};
// Any change to either Authors or Books will trigger reindexing
}
}public class Authors_ByBooks_JS : AbstractJavaScriptIndexCreationTask
{
public Authors_ByBooks_JS()
{
Maps = new HashSet<string>()
{
// For each Book ID, call 'load' and index the book's name
@"map('Author', function(author) {
return {
Books: author.BooksIds.map(x => load(x, 'Books').Name)
}
})"
// Any change to either Authors or Books will trigger reindexing
};
}
}The query:
- We can now query the index for Author documents by a book's name,
i.e. get all Authors that have the specified book's name in their list.
// Get all authors that have books with title: "The Witcher"
IList<Author> matchingAuthors = session
.Query<Authors_ByBooks.IndexEntry, Authors_ByBooks>()
.Where(x => x.BookNames.Contains("The Witcher"))
.OfType<Author>()
.ToList();// Get all authors that have books with title: "The Witcher"
IList<Author> matchingAuthors = await asyncSession
.Query<Authors_ByBooks.IndexEntry, Authors_ByBooks>()
.Where(x => x.BookNames.Contains("The Witcher"))
.OfType<Author>()
.ToListAsync();// Get all authors that have books with title: "The Witcher"
from index "Authors/ByBooks"
where BookNames = "The Witcher"Tracking implications
-
Indexing related data with tracking can be a useful way to query documents by their related data.
However, that may come with performance costs. -
Re-indexing will be triggered whenever any document in the collection that is referenced by
LoadDocumentis changed. Even when indexing just a single field from the related document, any change to any other field will cause re-indexing. (See changes that cause re-indexing here). -
Frequent re-indexing will increase CPU usage and reduce performance,
and index results may be stale for prolonged periods. -
Tracking indexed related data is more useful when the indexed related collection is known not to change much.
Document changes that cause re-indexing
-
The following changes done to a document will trigger re-indexing:
- Any modification to any document field (not just to the indexed fields)
- Adding/Deleting an attachment
- Creating a new Time series (modifying existing will not trigger)
- Creating a new Counter (modifying existing will not trigger)
-
Any such change done either on any document in the indexed collection or in the indexed related documents will trigger re-indexing.
LoadDocument syntax
Syntax for LINQ-index:
T LoadDocument<T>(string relatedDocumentId);
T LoadDocument<T>(string relatedDocumentId, string relatedCollectionName);
T[] LoadDocument<T>(IEnumerable<string> relatedDocumentIds);
T[] LoadDocument<T>(IEnumerable<string> relatedDocumentIds, string relatedCollectionName);Syntax for JavaScript-index:
object load(relatedDocumentId, relatedCollectionName);| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| relatedDocumentId | string |
ID of the related document to load |
| relatedCollectionName | string |
The related collection name |
| relatedDocumentIds | IEnumerable<string> |
A list of related document IDs to load |