Create Map Index
-
A Map index consists of one or more LINQ-based or JavaScript mapping functions that indicate how to index selected document fields, counters, and time series data.
-
In this page:
Edit Index View
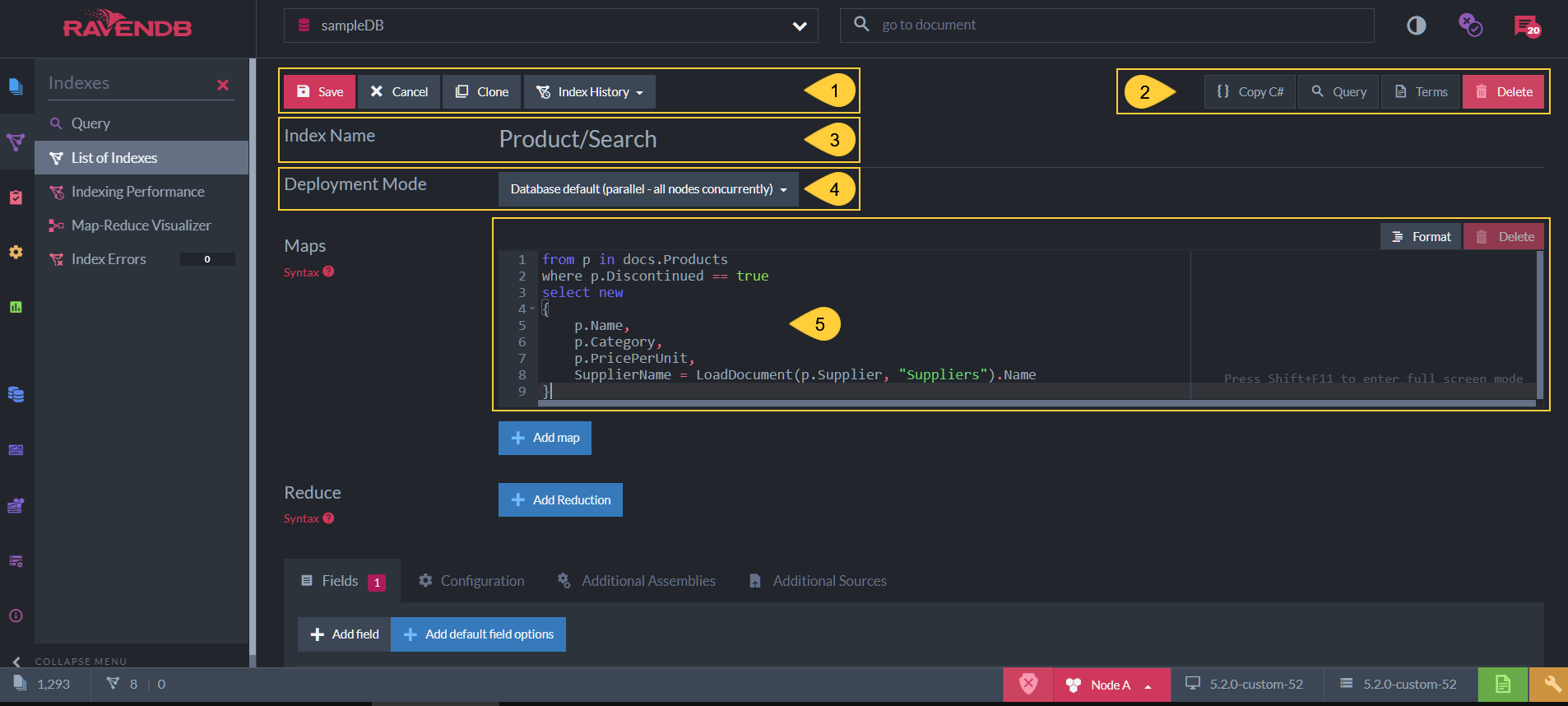
Figure-1: Edit Index View
-
Save - Save index definition.
Cancel - Return to Index List View without creating or changing the index definition.
Clone - Clone this index (available for an already saved index).
Index History - Open the Index History Dialog. -
Options available for an already saved index:
Copy C# - Click to view and copy the C# class that defines the index as set in the Studio.
Query - Click to go the the Query View and query this index.
Terms - Click to see the index terms, see below.
Delete - Delete this index. -
Index Name - An index name can be composed of letters, digits,
.,/,-, and_. The name must be unique in the scope of the database.- Uniqueness is evaluated in a case-insensitive way - you can't create indexes named both
usersbynameandUsersByName. - The characters
_and/are treated as equivalent - you can't create indexes named bothusers/bynameandusers_byname. - If the index name contains the character
., it must have some other character on both sides to be valid././is a valid index name, but./,/., and/../are all invalid.
- Uniqueness is evaluated in a case-insensitive way - you can't create indexes named both
-
Deployment Mode - Select the index deployment mode.
- Database default (parallel - all nodes concurrently)
With this option, the deployment mode will be the Default Mode defined on the database. - Rolling (one node at a time)
The index will be deployed on the cluster nodes in a linear order, one node at a time. - Parallel (all nodes concurrently)
The index will be deployed on all cluster nodes in parallel. - Read more about deployment modes here.
- Database default (parallel - all nodes concurrently)
-
The Map Function of the index.
-
In the above example, the index will go over documents from the
Productscollection and will only index documents whoseDiscontinuedproperty is 'true'. -
Note: The range of documents from which the query on this index will supply results will be on only Products collection documents that have 'true' in the 'Discontinued' document field property. If the index was defined without the 'where' clause, but only using 'from p in docs.Products', then the documents range for the query result would have been the whole Products collection.
-
Each Index Entry that will be created for this index will be composed of the following 4 fields:
Name,Category,PricePerUnit&SupplierName.
The first 3 are taken directly from the document fields, while SupplierName is a calculated index field.
The supplier's name is derived from the Name field that is taken from the loaded supplier document. -
At query time, when querying this index, the resulting documents can be searched on and further filtered
by these Index Fields defined and by the created Terms. See the query results on this index in Query View. -
See more Map-Indexes examples in Map Index defined from Code
-
Index Fields & Terms
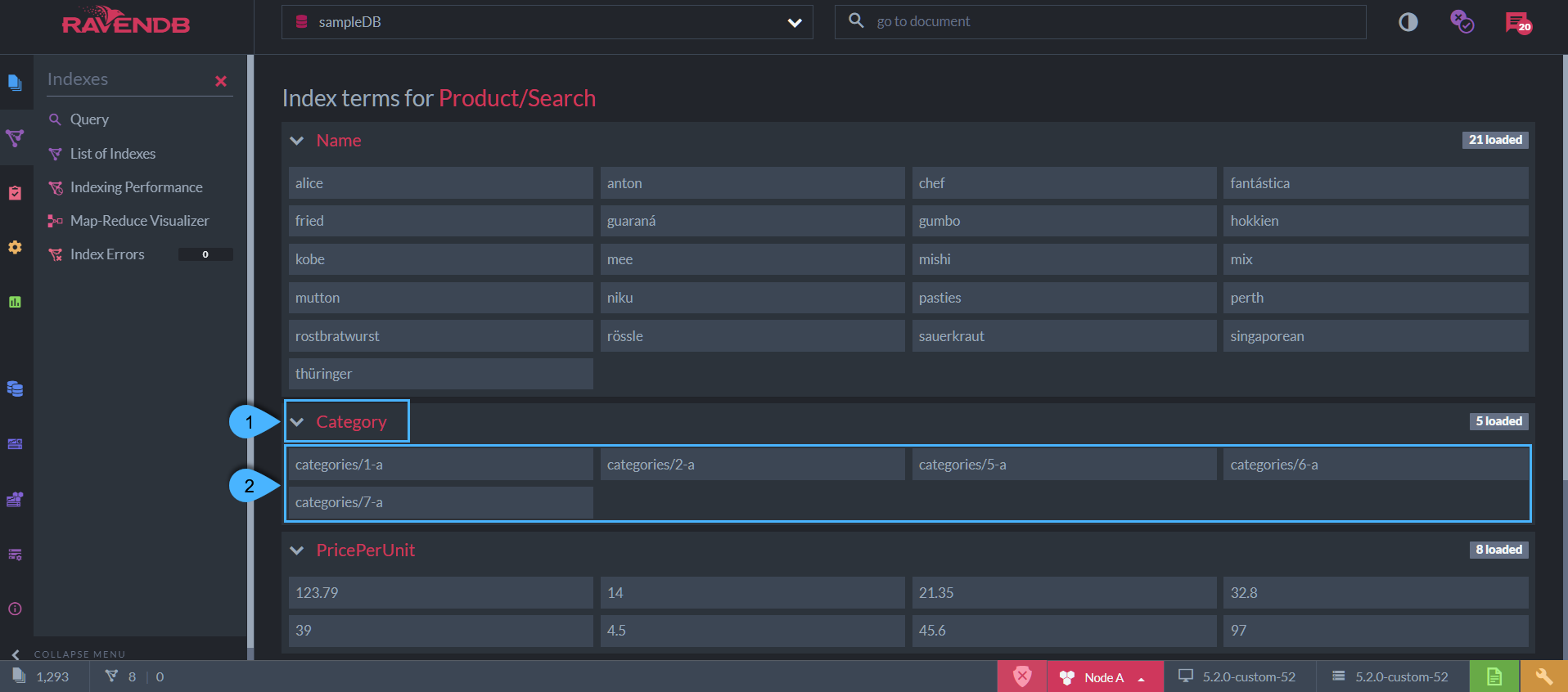
Figure-2: Index Fields & Terms
-
Index Fields
The index-fields that are indexed per index-entry with the above index-definition are:
Name,Category,PricePerUnit&SupplierName. -
Terms
The terms are listed under each field.
The terms are created from the value of the field that was requested to be indexed according to the specified Field Options.
Index Field Options
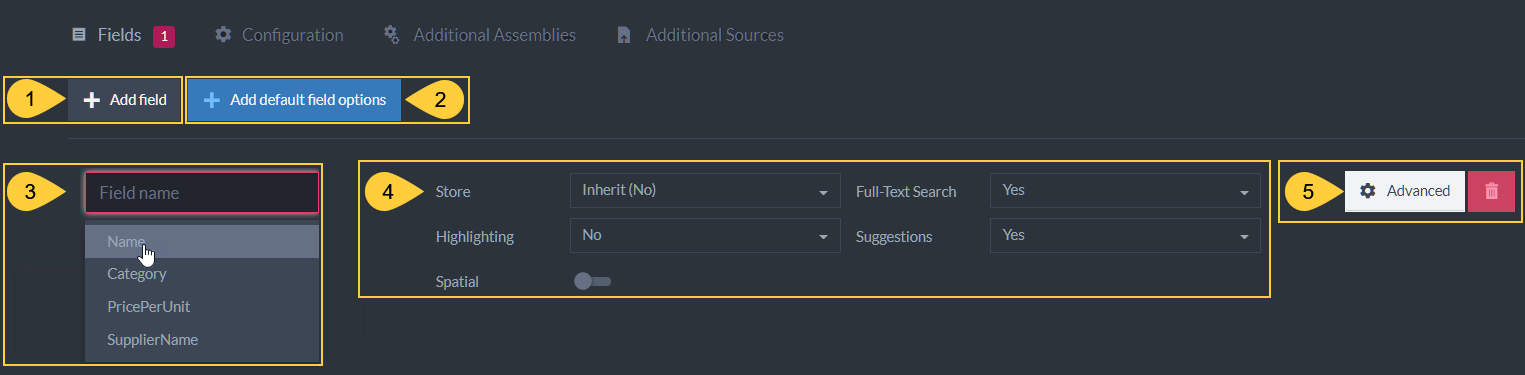
Figure-3a: Index Field Options
-
Add field
Create indexing options for one document field in the collection this index applies to. -
Add default field options
Set default index field options for all indexed fields. See below. -
Select Field
Select a field from the drop-down. The options for this will override the default options. -
-
Store- Setting 'Store' will store the value of this field in the index itself.
At query time, if 'Store' is set, then the value is fetched directly from the index, instead of from the original document.
If the field value is not stored in the index then it will be fetched from the document.
Storing data in the index will increase the index size.
Learn more in Storing Data in Index. -
Full-Text-Search- Set this to 'Yes' to allow searching for strings inside the text values of this field.
The terms that are indexed are tokens that are split from the original string according to the specified Analyzer.
The Analyzer is set in the 'Indexing' dropdown. The default analyzer is a simple case-insensitive analyzer. -
Highlighting- Set to 'Yes' to enable Highlighting. Requires Storage to be set to 'Yes'. In the advanced options, Indexing needs to be set to 'Search' and Term Vector set to 'WithPositionsAndOffsets'. -
Suggestions- Setting 'Suggestions' will allow you to query what the user probably meant to ask about. i.e. spelling errors.
Learn more in this Blog Post, and in Querying: Suggestions. -
Spatial- See below
-
-
Advanced
Set advanced indexing options for the selected field.
Advanced Index Field Options:
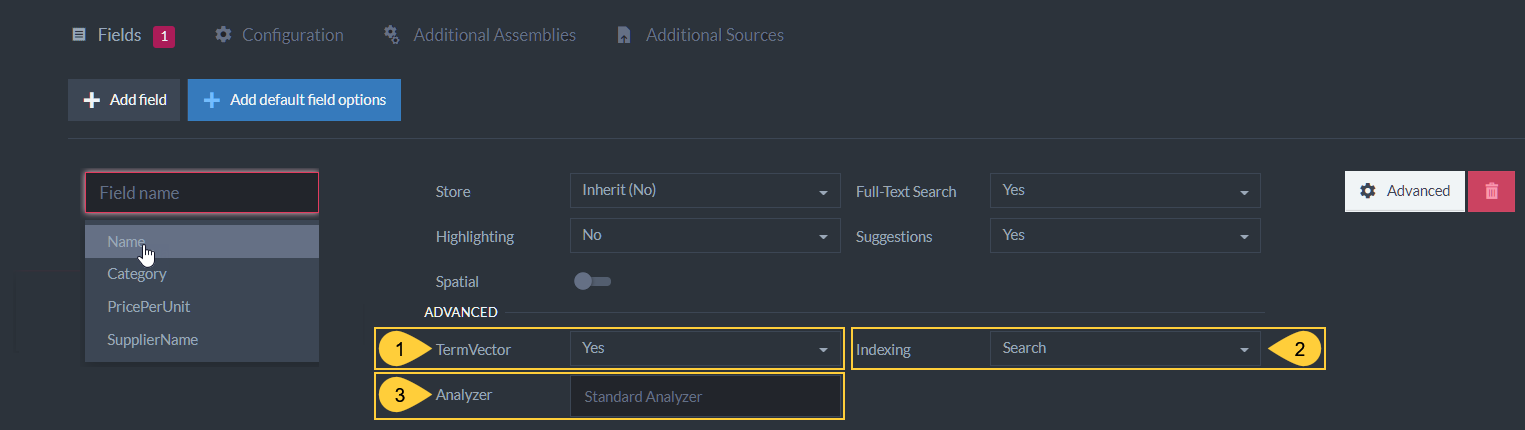
Figure-3b: Advanced Index Field Options
-
Term Vector- Term Vectors are used in RavenDB's query feature More Like This, which suggests documents that are similar to a selected document, based on shared indexed terms. i.e. suggest similar catalogs.
A 'Term Vector' for a text paragraph will contain a list of all unique words and how often they appeared.
Set 'full-text-search' on the field (index entry) and define it to have a 'Term Vector'.
Learn more in Indexes: Term Vectors, and in this Blog Post. -
Indexing- This setting determines which Analyzer can be used:- Exact - The 'Keyword Analyzer' is used. The text is not split into tokens, the entire value of the field is treated as one token.
- Default - The 'LowerCase Keyword Analyzer' is used. The text is not split into tokens. The text is converted to lower-case, and matches are case insensitive.
- Search - Select an analyzer to use from the dropdown menu. If you set Indexing to 'Search' and do not select an analyzer, the analyzer is 'StandardAnalyzer' by default. Whenever you create a custom analyzer, it is added to this dropdown menu.
Default Index Field Options:
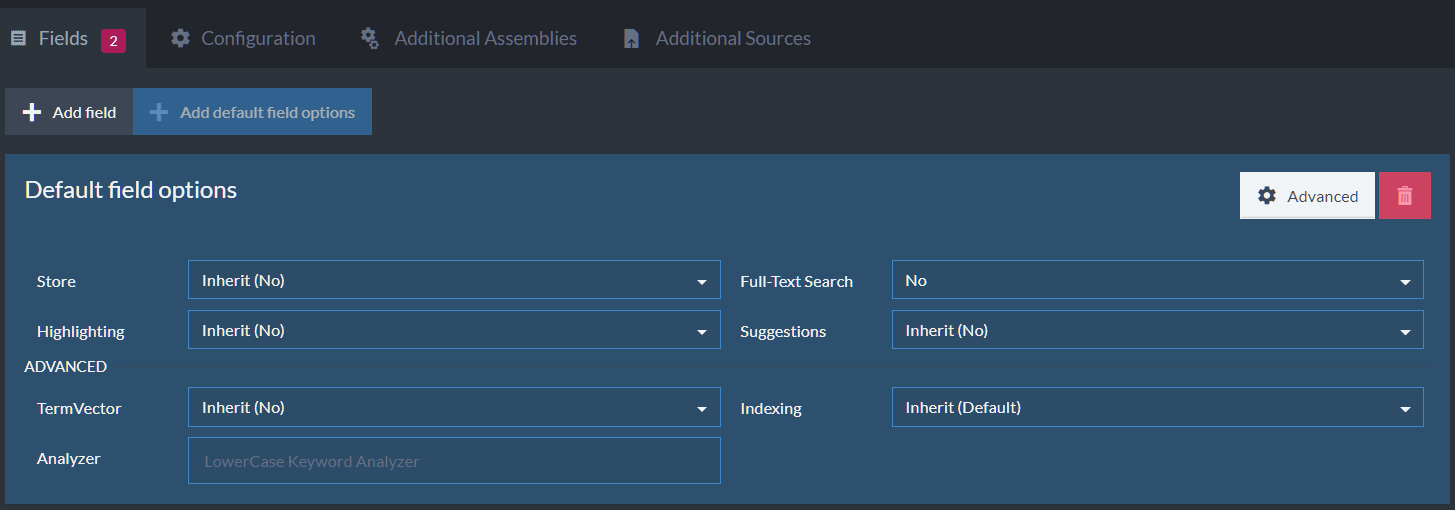
Figure-3c: Default Index Field Options
Configuration
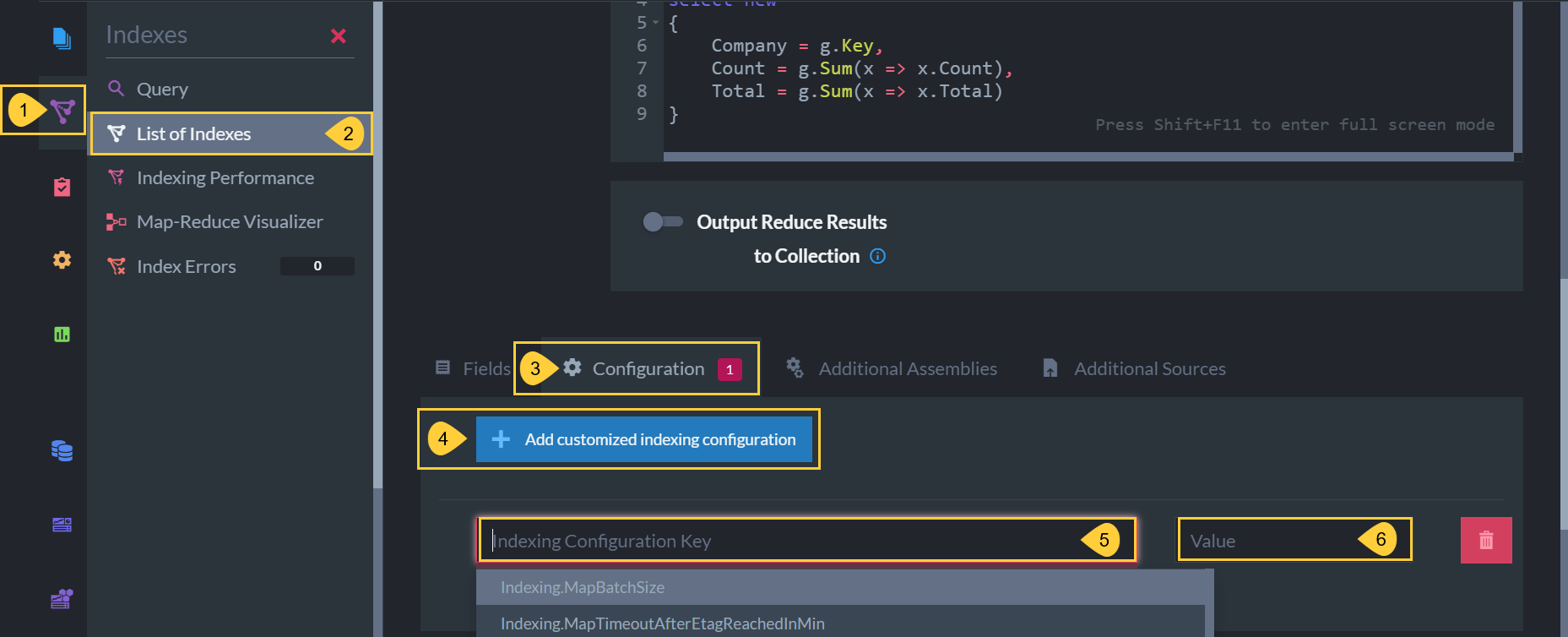
Setting Configuration via Studio
- Indexes Tab
Click to see indexing options. - List of Indexes
Select to see the list of your current indexes.
You can only configure static-indexes, not auto-indexes.
Select the index for which you want to customize the default configuration. - Configuration
Scroll down and select the Configuration tab. - Add customized indexing configuration
Click to add a configuration key. - Indexing Configuration Key
Paste or select the configuration key that you want to set.
You can set any indexing configuration that has a "per-index" scope. - Value
Enter the new value for this configuration key.
Click Save at the top of the interface when done.
Additional Assemblies
Use the Additional Assemblies
feature to enhance Index capabilities with classes and methods taken from libraries.
In the below example, Path.GetFileName can be used by the index map method because the
runtime library System.IO is added as an additional assembly.
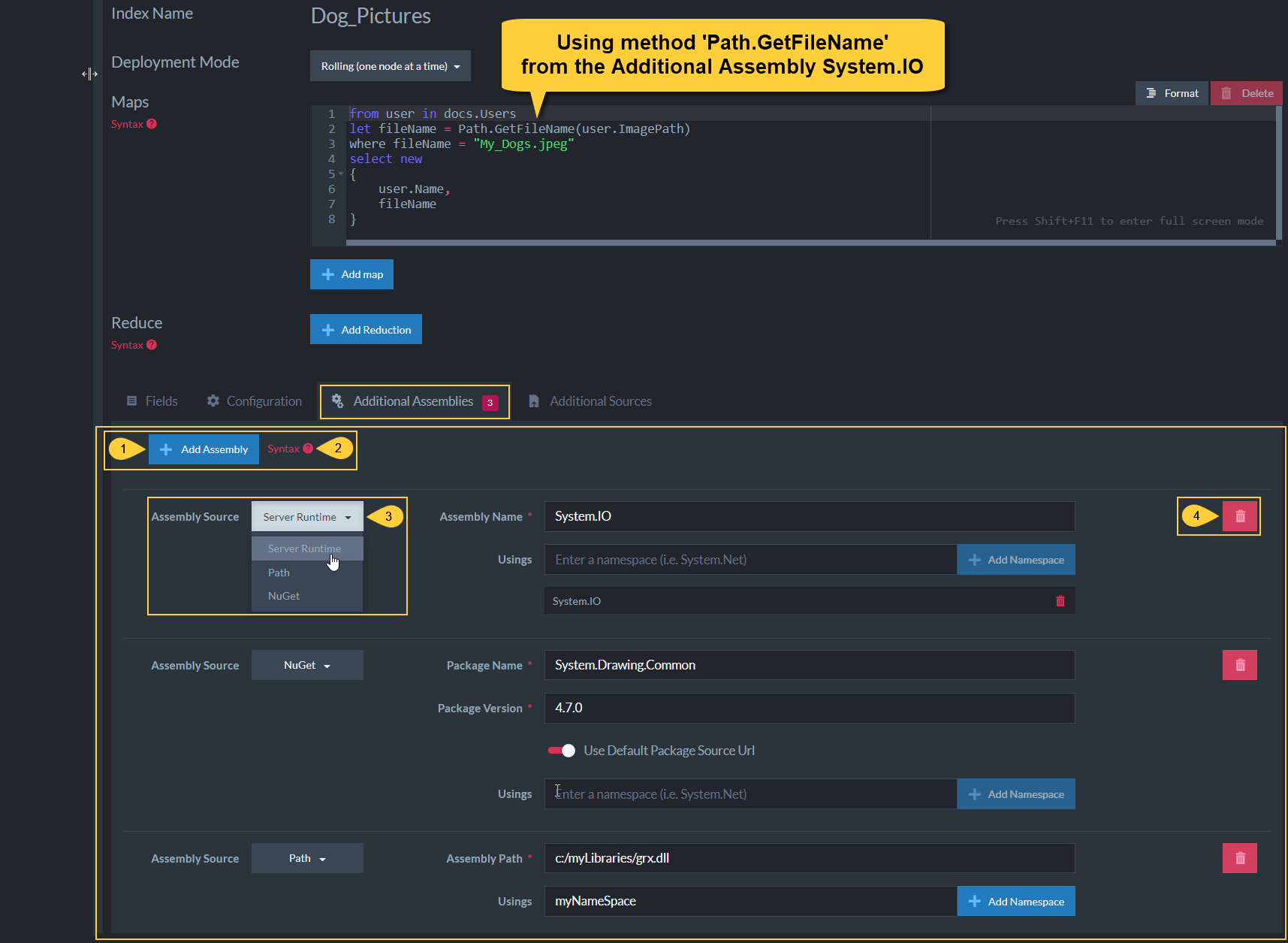
Figure-5: Additional Assemblies
-
Add Assembly
Click to add an assembly source for your index usage. -
Syntax
See syntax samples. -
Assembly Source
Select the assembly source type.
Added assemblies can be -- Server Runtime - a runtime library.
- Path - The path to a library file on your local disk.
- Nuget - a Nuget package.
Note that additional assemblies are allowed to include pre-release packages.
-
Remove Assembly
Click to remove the assembly.
Server Runtime Library

Figure-6: Server Runtime Library
-
Assembly Source
In this example, the assembly is a runtime library. -
Assembly Name
The name of the runtime library you want to use. -
Usings
Optionally, choose a namespace within the assembly. -
Add Namespace
Click to add the namespace to the list ofUsings. -
Namespaces list
The list of namespaces used. -
Remove Namespace
Click to remove this namespace from the list. -
Remove Assembly
Click to remove this assembly.
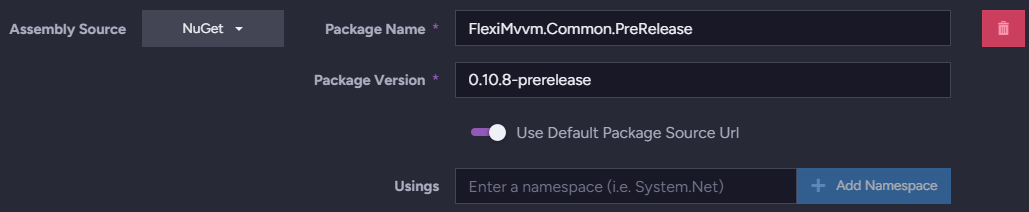
Nuget Package
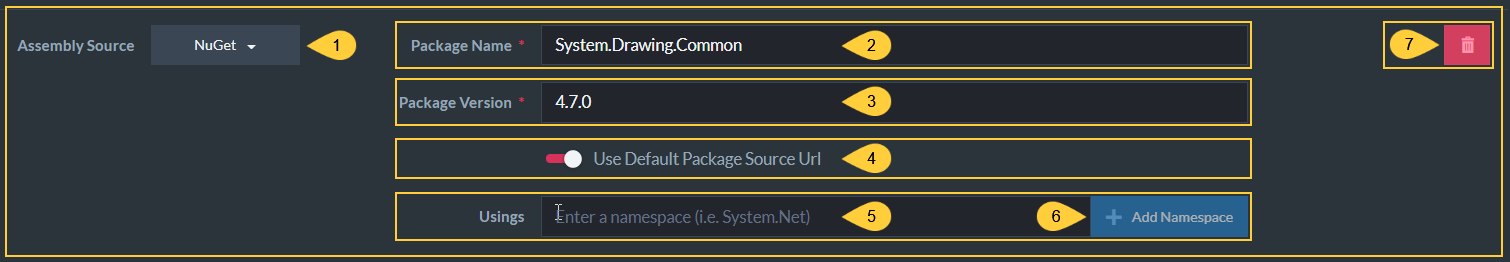
Figure-7: Nugat Package
-
Assembly Source
In this case, Nuget was chosen so the index can use classes and methods taken from a Nuget package. -
Package Name
Nuget package name. -
Package version
Nuget package version. -
Default Package Source URL
- Toggle ON to use the package default URL.
- Toggle OFF to provide the URL yourself.
-
Usings
Optionally, choose a namespace within the Nuget package. -
Add Namespace
Click to add the namespace to the list ofUsings. -
Remove Assembly
Click to remove this assembly.
Local Library Path

Figure-8: Local Library Path
-
Assembly Source
In this case, Path was chosen so the index can use classes and methods taken from a local library. -
Assembly Path
Provide a path to the local library file. -
Usings
Optionally, choose a namespace within the local library. -
Add Namespace
Click to add the namespace to the list ofUsings. -
Remove Assembly
Click to remove this assembly.
Additional Sources
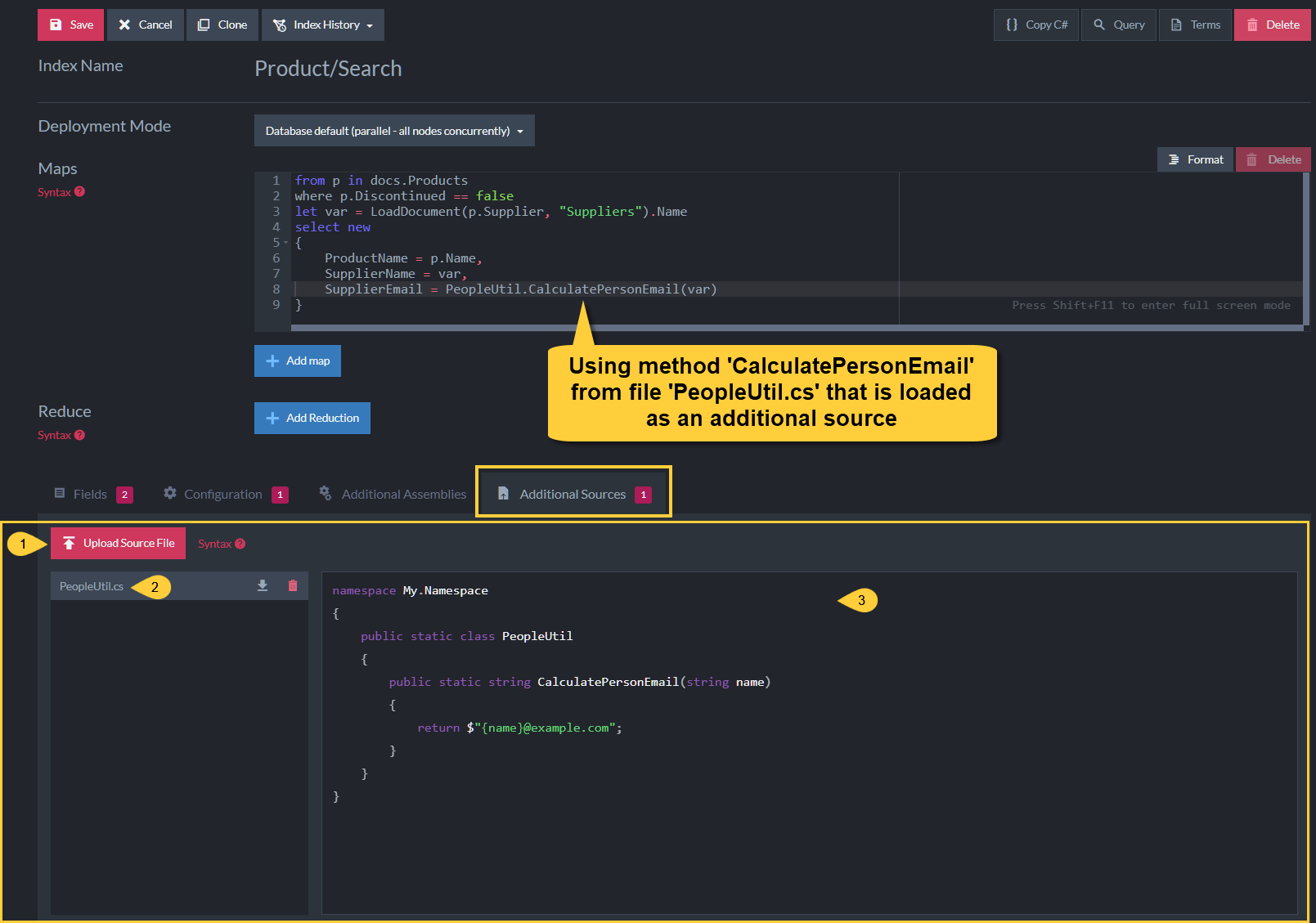
Figure-9: Additional Sources
You can extend the logic of the Map & Map-Reduce methods by referencing classes and methods from additional source files. This enables advanced scenarios since complex logic can be performed during the indexing process.
In the above example, file 'PeopleUtil.cs' was uploaded and method 'CalculatePersonEmail' is used to calculate the index entry 'SupplierEmail'.
- Upload Source File
Click to upload a file from the file system that contains classes and methods you want to use. - Uploaded File
The file that has been uploaded whose contents can be used within the index methods. - Source Code
Read-only view of the uploaded file's source code.
Spatial Field Options
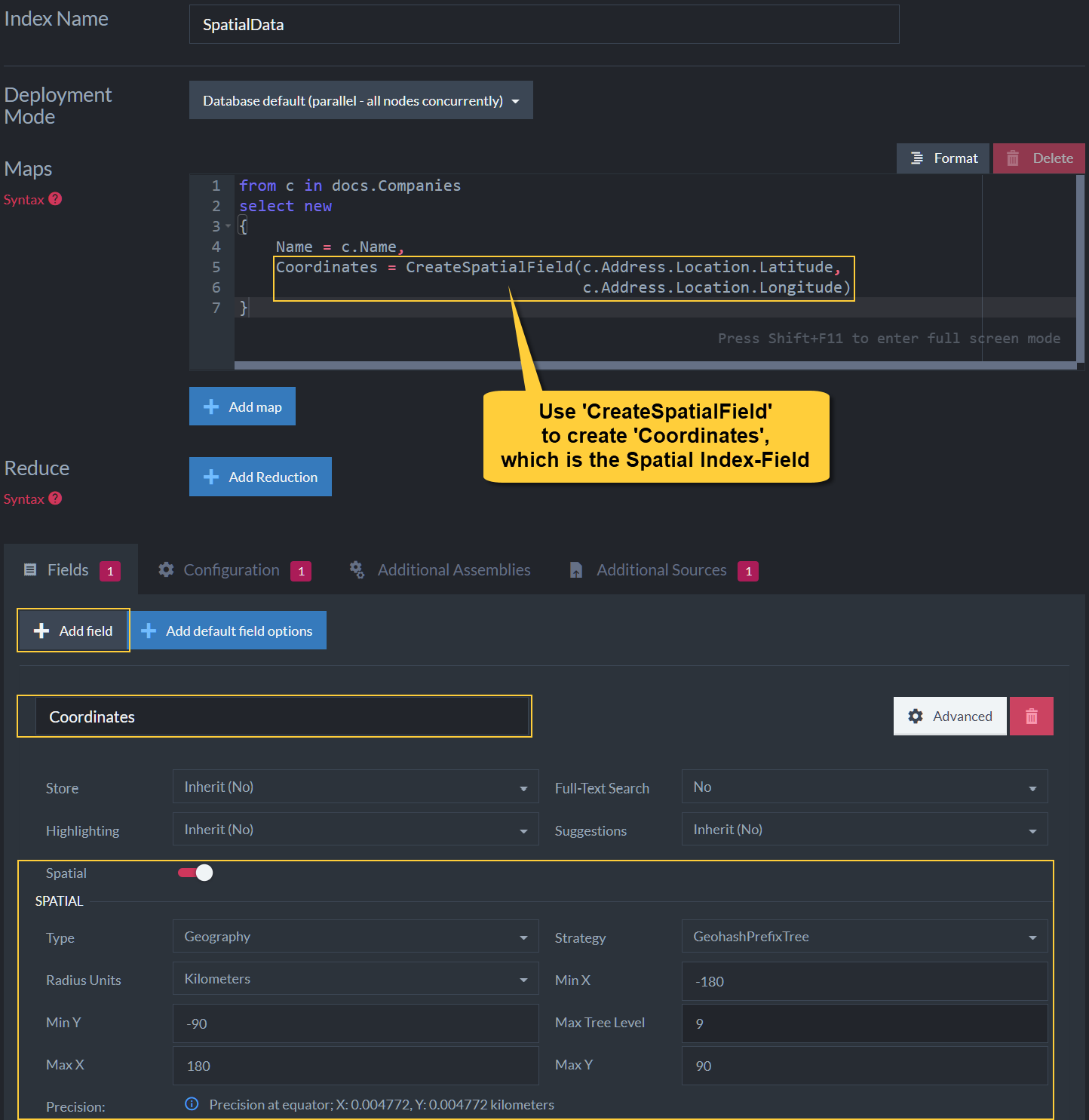
Figure-10: Spatial Field Options
-
Spatial Field
Spatial searches allow you to search using geographical data.
In order to be able to do such searches, a spatial index field has to be defined. -
CreateSpatialField()
This method instructs RavenDB to use the provided longitude and latitude from the document field properties and create the spatial field named 'Coordinates'. Spatial queries can then be made on the 'Coordinates' field. -
Spatial Type
RavenDB supports both the 'Geography' and 'Cartesian' systems. -
Spatial Indexing Strategy
'Strategy' determines the format of the indexed term values.
The following indexing strategies are supported:
• Bounding box
• Geohash prefix tree
• Quad prefix tree -
Radius Units
Set the units (miles, kilometers) to be used when querying with RQL 'spatial.circle'.
Learn more about querying spatial fields in: Querying: Spatial. -
Max Tree Level
Control how precise the spatial queries are going to be. -
X & Y Min & Max Values
Setting the min & max values for X & Y is relevant only for the 'Cartesian' system type. -
Learn more about spatial indexes in: Indexing: Spatial.