Search Engine: Corax
-
Corax is RavenDB's native search engine, introduced in RavenDB version 5.4 as an in-house searching alternative for Lucene.
Lucene remains available as well; you can use either Corax or Lucene as your search engine, as you prefer.Corax is still an experimental feature. To use it, you must enable experimental features first.
-
The main role of the database's search engine is to satisfy incoming queries.
In RavenDB, the search engine achieves this by handling each query via an index.
If no relevant index exists, the search engine will create one automatically.The search engine is the main "moving part" of the indexing mechanism, that processes and indexes documents by index definitions.
-
The search engine can be selected separately for auto and static indexes.
-
The search engine can be selected per server, per database, and per index (for static indexes only).
-
In this page:
Enabling Corax
Corax is an experimental feature and is disabled by default.
To use it, you must explicitly enable RavenDB's experimental features.
-
To enable experimental features when RavenDB is already installed -
Edit RavenDB's configuration file and Enable experimental features.E.g. set
settings.jsonto:
{ "ServerUrl": "http://127.0.0.1:8080", "Setup.Mode": "None", // enable experimental features "Features.Availability": "Experimental" }You must restart the server after making these changes, for the new settings to be read and applied.
-
To enable experimental features during Setup -
check Enable the following experimental features in the Welcome page.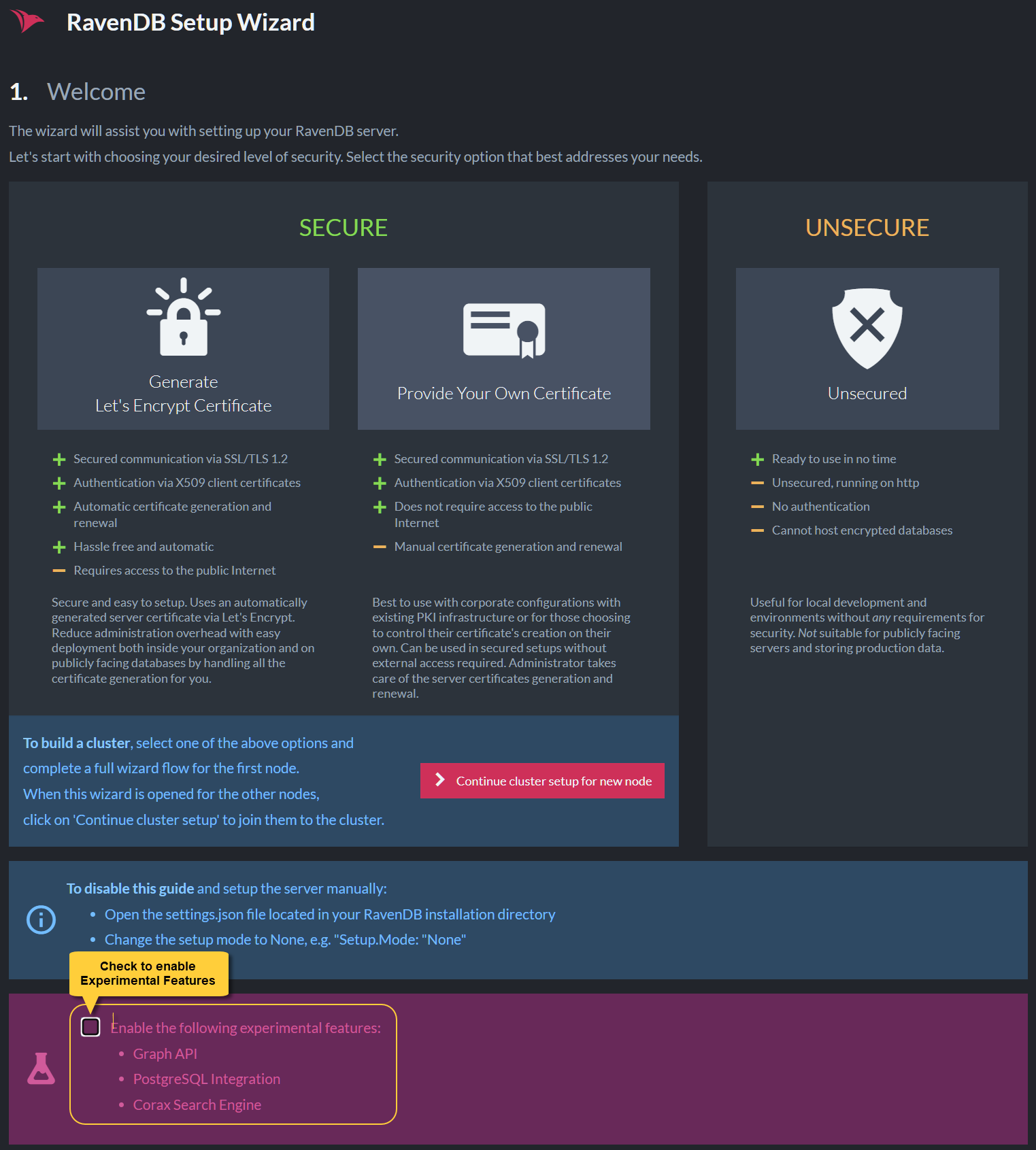
Enable Experimental Features
Selecting the Search Engine
-
You can select your preferred search engine in several scopes:
- Server-wide, selecting which search engine will be used by all the databases hosted by this server.
- Per database, overriding server-wide settings for a specific database.
- Per index,
overriding server-wide and per-database settings.
Per-index settings are available only for static indexes.
-
Two configuration options are available:
- Indexing.Auto.SearchEngineType
Use this option to select the search engine (eitherLuceneorCorax) for auto indexes.
The search engine can be selected server-wide or per database. - Indexing.Static.SearchEngineType
Use this option to select the search engine (eitherLuceneorCorax) for static indexes.
The search engine can be selected server-wide, per database, or per index.
- Indexing.Auto.SearchEngineType
Select Search Engine: Server Wide
Select the search engine for all the databases hosted by a server
by modifying the server's settings.json file.
E.g. -
{
"Indexing.Auto.SearchEngineType": "Corax"
"Indexing.Static.SearchEngineType": "Corax"
}You must restart the server for the new settings to be read and applied.
Select Search Engine: Per Database
To select the search engine that the database would use, modify the relevant Database Record settings. You can easily do this via Studio:
-
Open Studio's Database Settings page, and enter
SearchEnginein the search bar to find the search engine settings.
ClickEditto modify the default search engine.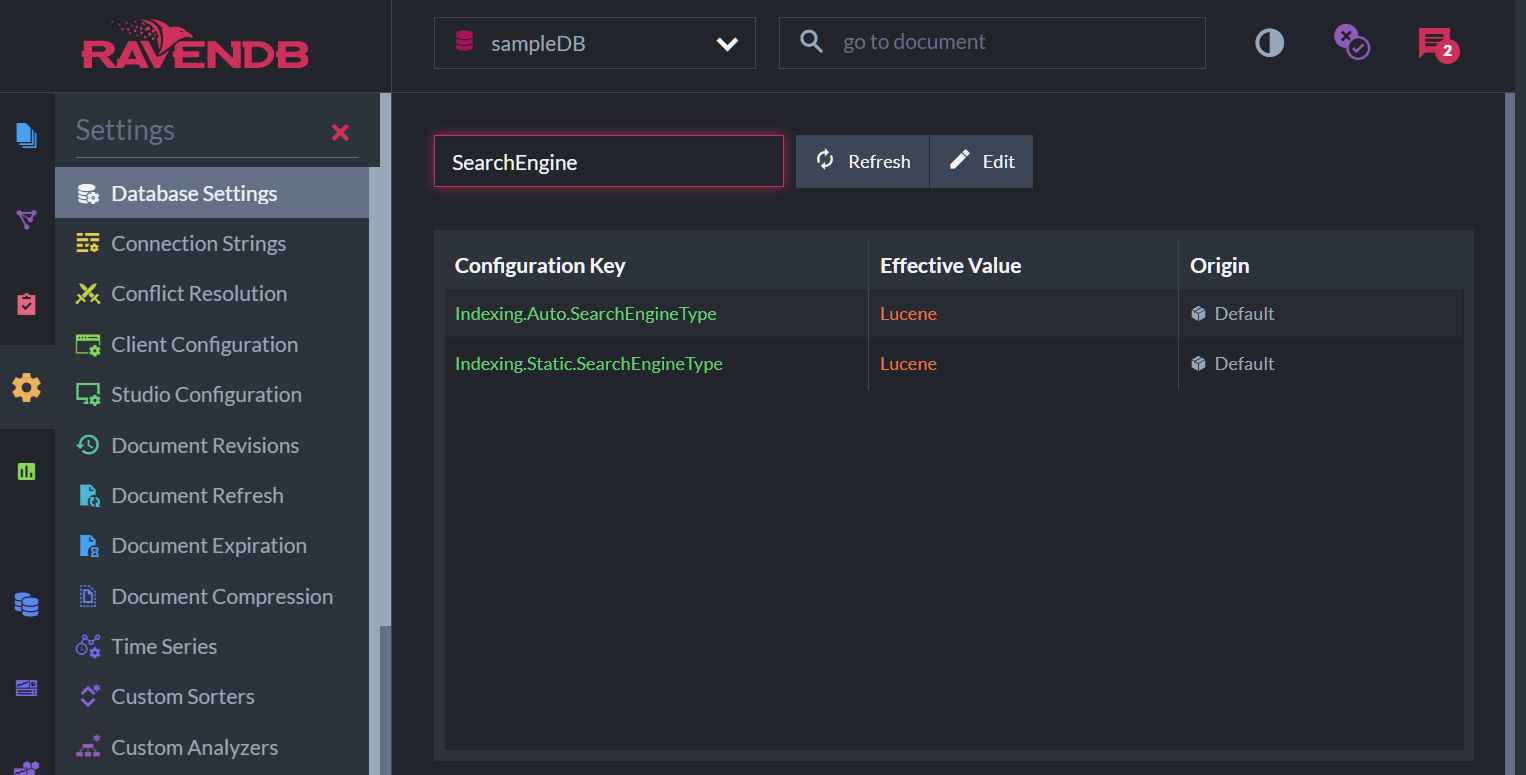
Database Settings
-
Select your preferred search engine for Auto and Static indexes.
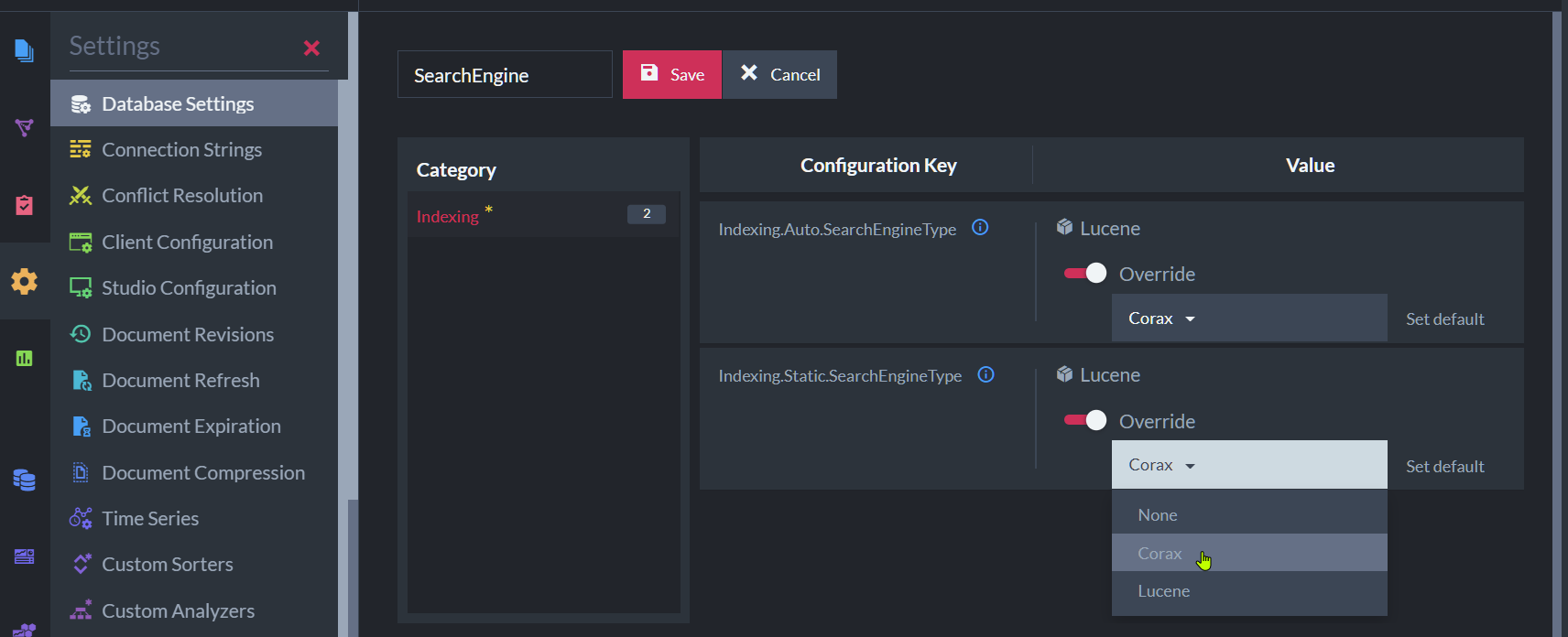
Corax Database Options
-
To apply the new settings either disable and re-enable the database or restart the server.

Default Search Engine
Select Search Engine: Per index
You can also select the search engine that would be used by a specific index, overriding any per-database and per-server settings.
Select Index Search Engine via Studio:
-
Indexes-List-View > Edit Index Definition
Open Studio's Index List view and select the index whose search engine you want to set.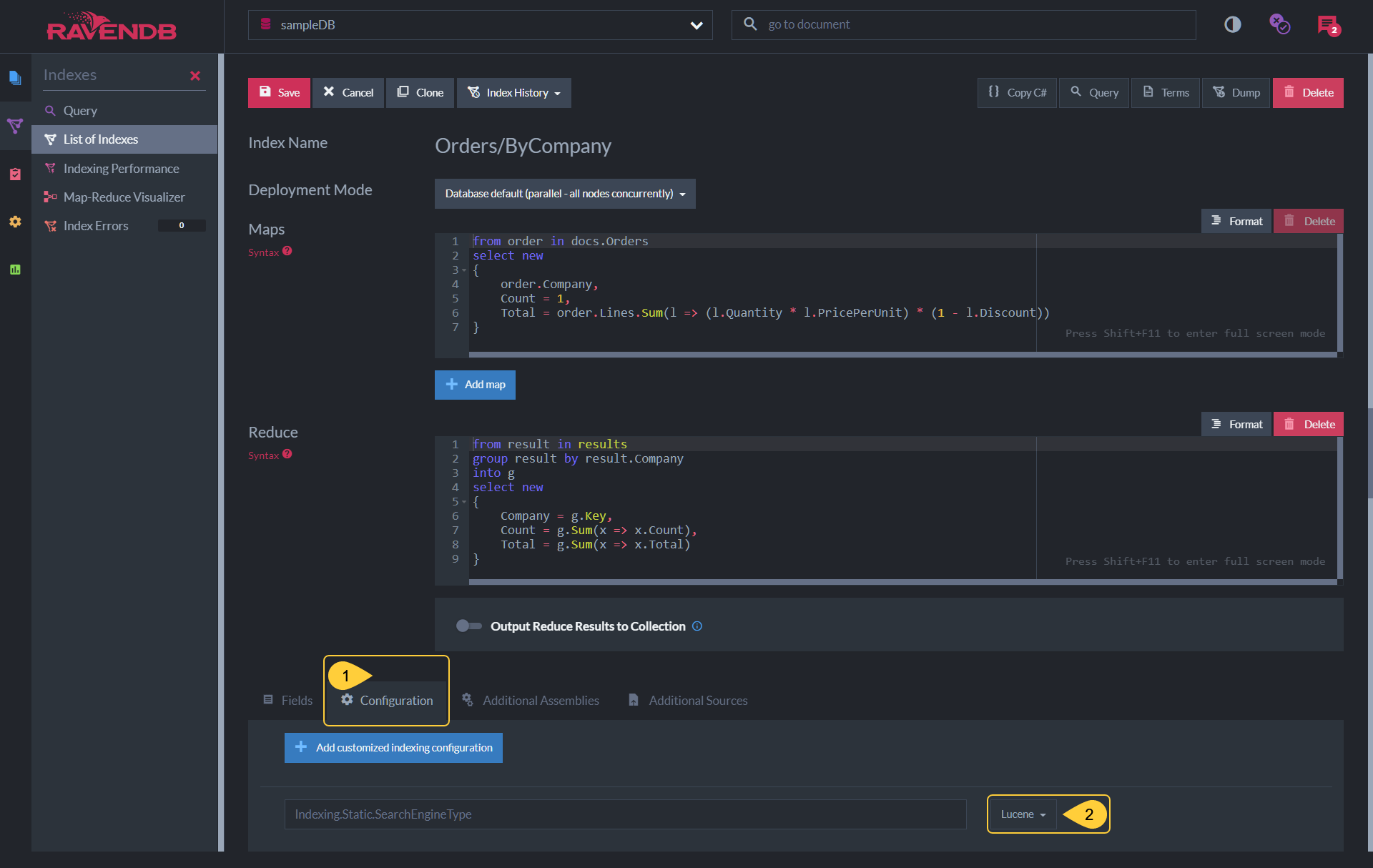
Index Definition
- Open the index' Configuration tab.
- Select the search engine you prefer for this index.
-
The indexes list view will show the changed configuration.
Search Engine Changed
Select Index Search Engine using Code
While defining an index using the API, use the SearchEngineType
property to select the search engine that would run the index.
Available values: SearchEngineType.Lucene, SearchEngineType.Corax.
- You can pass the search engine type you prefer:
// set search engine type while creating the index new Product_ByAvailability(SearchEngineType.Corax).Execute(store); - And set it in the index definition:
private class Product_ByAvailability : AbstractIndexCreationTask<Product> { public Product_ByAvailability(SearchEngineType type) { // Any Map/Reduce segments here Map = products => from p in products select new { p.Name, p.Brand }; // The preferred search engine type SearchEngineType = type; } }
Supported Features
Corax supports Auto and Static indexing.
The feature is currently under construction, please find its full list of supported and yet-unsupported features below.
-
While indexing, Corax does not support:
- Boosting
- WKT shapes
(when spatial data is indexed, spatial points Are indexed while WKT shapes are Not indexed.)
-
While querying, Corax does not support:
- MoreLikeThis
- Facets
- Fuzzy Search
- Searching by Regex
- Corax does not support Dynamic Fields yet.
As a result, the many Javascript indexes that use dynamic fields are not supported.
| Query Term | Method / Keyword | Supported by Corax |
|---|---|---|
| WHERE | ||
| id() | yes |
|
| search() | yes |
|
| cmpxchg() | no | |
| boost() | yes |
|
| regex() | no | |
| startsWith() | yes |
|
| endsWith() | yes |
|
| lucene() | no | |
| exists() | yes |
|
| exact() | yes |
|
| intersect() | no | |
| spatial.within() spatial.contains() spatial.disjoint() spatial.intersects() |
yes yes yes yes |
|
| moreLikeThis() | no |
| Query Term | Method / Keyword | Supported by Corax |
|---|---|---|
| ORDER BY | ||
| ASC / ASCENDING | yes |
|
| DESC / DESCENDING | yes |
|
| AS | yes |
|
| string | yes |
|
| long | yes |
|
| double | yes |
|
| alphaNumeric | yes |
|
| random() | no | |
| score() | yes |
|
| spatial.distance() | yes |
Unimplemented Methods
Trying to use Corax with an unimplemented method (see
Supported Features above)
will generate a System.NotImplementedException exception and end the search.
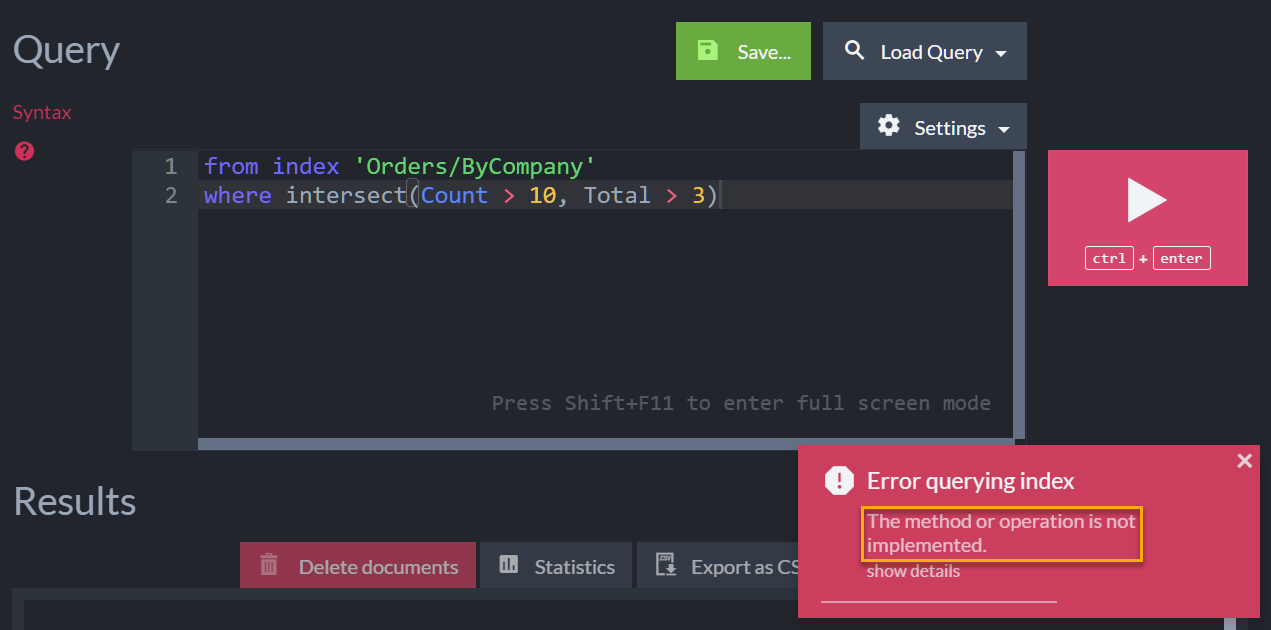
E.g. -
the following query uses the intersect method, which is currently not supported by Corax.
from index 'Orders/ByCompany'
where intersect(Count > 10, Total > 3)If you set Corax as the search engine for the Orders/ByCompany index
used by the above query, running the query will generate the following
exception and the search will stop.
Handling of Complex JSON Objects
Complex JSON properties cannot currently be indexed and searched by Corax.
Consider, for example, the following orders document:
{
"Company": "companies/27-A",
"Employee": "employees/2-A",
"ShipTo": {
"City": "Torino",
"Country": "Italy",
"Location": {
"Latitude": 45.0907661,
"Longitude": 7.687425699999999
}
}
}As the Location property of the document above contains not a simple numeric value
or string but a list of key/value pairs, attempting to index this field using Corax
would fail.
There are several ways to handle the indexing of complex JSON objects:
1. Index a Simple Property Contained in the Complex Field
Index one of the simple key/value properties stored within the nested object.
In the Location field, for example, Location's Latitude and Longitude.
can serve us this way:
from order in docs.Orders
select new
{
Latitude = order.ShipTo.Location.Latitude,
Longitude = order.ShipTo.Location.Longitude
}2. Index the Document Using Lucene
As long as Corax doesn't index complex JSON objects, you can always select Lucene as your search engine when you need to index nested properties.
3. Disable the Indexing of the Complex Field
You can use Corax as your search engine, but explicitly disable the indexing
of complex objects.
When you disable the indexing of a field this way, the field's contents
can still be stored and projected.
-
To disable indexing for a specified field via Studio:
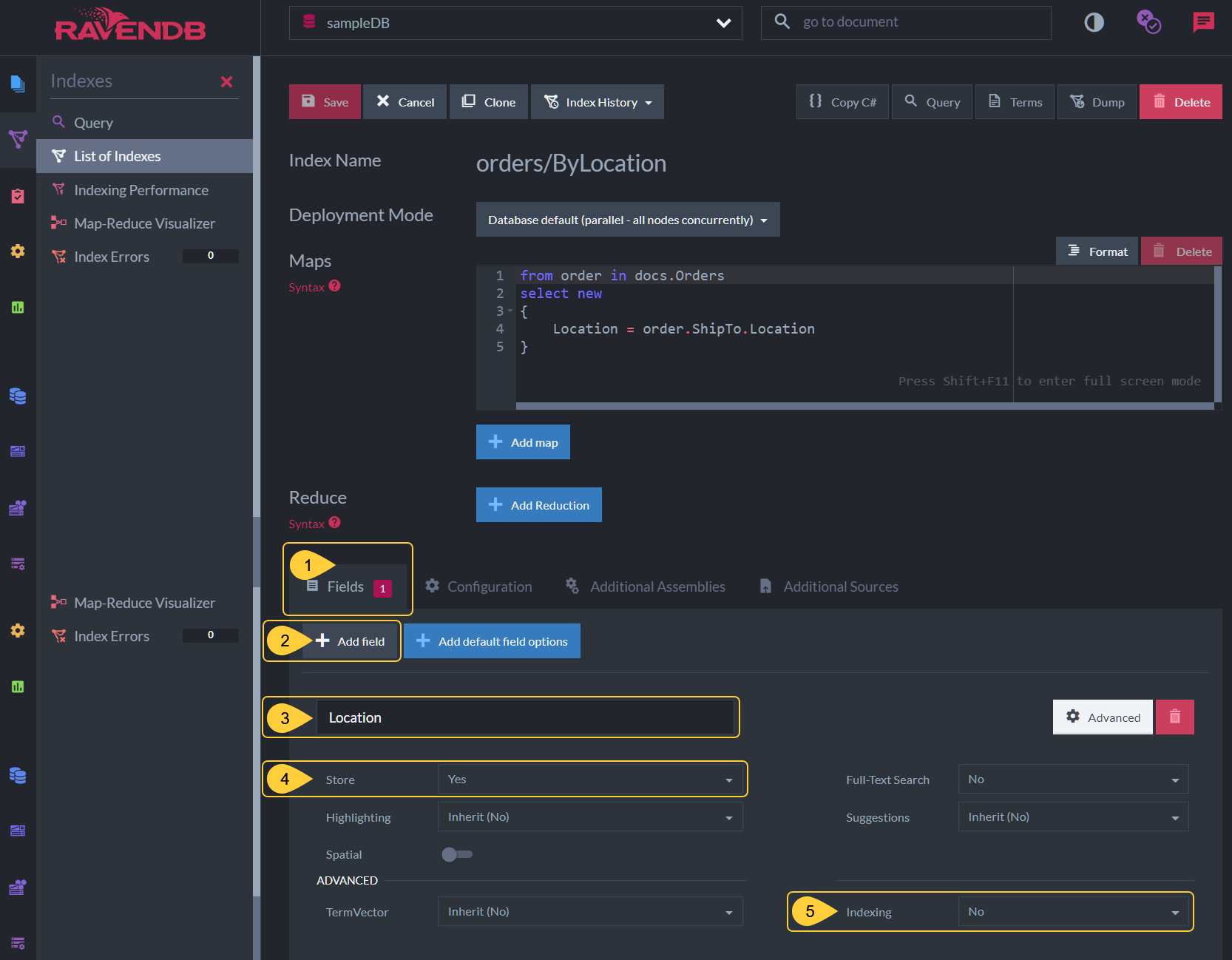
- Open the index definition's Fields tab.
- Click Add Field to specify what field Corax shouldn't index.
- Enter the name of the field Corax should not index.
- Can only be set to Yes when Corax is used since Corax always stores fields.
- Select No to disable indexing for the specified field.
-
To disable indexing for a specified field using Code:
private class Order_ByLocation : AbstractIndexCreationTask<Order> { public Order_ByLocation(SearchEngineType type) { Map = orders => from o in orders select new { o.ShipTo.Location }; SearchEngineType = type; // Disable Indexing for this field Index("Location", FieldIndexing.No); // Enable storing the field's contents // (this is mandatory if its indexing is disabled) Store("Location", FieldStorage.Yes); } }
4. Turn the complex property into a string
You can use ToString() to index the complex property as a string.
from order in docs.Orders
select new
{
// this will fail for the above document when using Corax
Location = order.ShipTo.Location
}from order in docs.Orders
select new
{
// handling the field as string will allow Corax to index it
Location = order.ShipTo.Location.ToString()
}Using ToString will serialize all the properties of the complex property into
a single string, including names, values, brackets, and so on.
The produced string is not a good feed for analyzers and is not commonly used for searches.
It does, however, make sense in some cases to project such a string.
If Corax Encounters a Complex Property While Indexing:
-
If an auto index exists for the document, Corax will throw
System.NotSupportedExceptionto notify the user that a search that makes no sense has been attempted. -
If a static index is used and it doesn't explicitly relate to the complex field, Corax will automatically exempt the field from indexing (by defining Indexing: No for this field as shown above).
If the static index explicitly sets the Indexing flag in any other way but "no", Corax will throw the exception.