Guides: Add RavenDB to an Existing Azure Functions Project (Node.js)
-
Microsoft Azure Functions is a serverless platform that supports multiple languages and frameworks that let you deploy workloads that scale without managing any infrastructure.
-
Learn more about how Microsoft Azure Functions work.
-
In this guide, you will learn how to connect to RavenDB from your existing Node.js Azure Functions.
We assume you are familiar with Node.js development techniques and the basics of Azure Function apps. -
In this page:
Before We Get Started
You will need the following before continuing:
- A RavenDB Cloud account or self-hosted client certificate
- Azure Function Core Tools 4.x+
- Node.js 18+
Starting from scratch?
For a brand new Azure Functions app, we recommend using the RavenDB Azure Functions Node.js template
which is set up with PEM certificate support.
You can also reference the template to see how the integration is set up.
Installing the RavenDB Client SDK
Get started by installing the ravendb npm package in your project which provides the Node.js client SDK.
Using npm:
npm install ravendb
Initializing the Document Store
Import the DocumentStore from ravendb package to create a new instance with the required
configuration and initialize your connection to RavenDB by calling the initialize method.
You can then export a function to initialize a document session to use in your Azure functions.
Example db.js Node module:
import { DocumentStore } from "ravendb";
const documentStore = new DocumentStore(
["https://a.free.mycompany.ravendb.cloud"],
"demo",
// authOptions
};
var initialized = false;
function initialize() {
if (initialized) return;
documentStore.initialize();
initialized = true;
}
export function openAsyncSession() {
if (!initialized) {
initialize();
}
return documentStore.openAsyncSession();
}For more on what options are available, see Creating a Document Store.
Warm vs. Cold Starts
In Azure Functions, the instance will be shared across function invocations if the Function is warmed up,
otherwise it will be constructed each time the function warms up. For more, see Deployment Considerations.
You can set options manually but it's more likely you'll want to configure support for app settings.
Adding Support for App Settings
You will need a way to pass options to the DocumentStore on your local machine and when deployed to Azure.
Node.js Azure Functions support a local.settings.json file which you can use to add additional settings locally. For example:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "node",
"DB_URLS": "https://a.free.company.ravendb.cloud",
"DB_NAME": "demo",
"DB_CERT_PATH": "../certs/company.client.certificate.pfx"
}
}You can then load environment variables through process.env:
import { readFileSync } from "fs";
import { DocumentStore } from "ravendb";
var documentStore;
var initialized = false;
function initialize() {
if (initialized) return;
const authOptions = {
type: "pfx",
// Read .pfx file using fs.readFileSync
certificate: readFileSync(process.env.DB_CERT_PATH)
};
documentStore = new DocumentStore(
process.env.DB_URLS.split(","), // Split by "," separator
process.env.DB_NAME,
authOptions
};
documentStore.initialize();
initialized = true;
}
export function openAsyncSession() {
if (!initialized) {
initialize();
}
return documentStore.openAsyncSession();
}
Configuring Support for Certificates
RavenDB uses client certificate authentication (mutual TLS) to secure your database connection.
The Node.js client SDK supports .pfx files or .pem files which is passed to the authOptions.certificate option.
There are multiple ways to load a certificate:
- Load from .pfx files
- Load from PEM-encoded certificate
- Load from Azure Key Vault
Load from .pfx Files
You can load PFX files with or without a password by providing the certificate buffer using authOptions.certificate:
const authOptions = {
type: "pfx",
// Read .pfx file using fs.readFileSync
certificate: readFileSync("../cert/company.client.certificate.pfx"),
// Optionally provide the password
password: "<CERT_PASSWORD>"
};
documentStore = new DocumentStore(
["https://a.free.company.ravendb.cloud"],
"demo",
authOptions
};
documentStore.initialize();If the .pfx file requires a password, provide it using password option.
However, keep in mind that using an absolute physical file path or a password
requires manual steps for every developer working on a project to configure.
Avoid uploading or deploying .pfx files
PFX files can be compromised, especially if they are not password-protected.
Using a physical file also makes it hard to manage and rotate when they expire.
They are only recommended for ease-of-use on your local machine.
For production, it is better to use the Certificate Store method or Azure Key Vault.
Load from PEM-encoded certificate
For Node.js-based Azure Functions, it's recommended to use a PEM-encoded certificate that can be provided through Azure app settings without deploying any files.
Unlike a .pfx file, a PEM-encoded certificate is plain-text encoded:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFCzCCAvO...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIJKAIBAAK...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----To pass a PEM-encoded certificate, you can read an environment variable like DB_CERT_PEM and
set authOptions using the pem certificate type:
const authOptions = {
type: "pem",
certificate: process.env.DB_CERT_PEM
};
documentStore = new DocumentStore(
["https://a.free.company.ravendb.cloud"],
"demo",
authOptions
};
documentStore.initialize();Normalizing PEM certificates
Be aware that the Azure portal removes line endings and you will need to manually normalize
the value for PEM parsing to succeed. If you are setting the value in the local.settings.json
file, you will need to format the value for JSON using a stringify tool.
Here is how the starter template adds support for loading certificates using a DB_CERT_PEM environment variable:
import { EOL } from "os";
import { readFile } from "fs/promises";
import { DocumentStore } from "ravendb";
let store;
let initialized = false;
export async function initializeDb({
urls,
databaseName,
dbCertPassword,
dbCertPath,
dbCertPem,
customize,
}) {
if (initialized) return;
let authOptions = undefined;
if (dbCertPath) {
authOptions = await getAuthOptionsFromCertificatePath(
dbCertPath,
dbCertPassword
);
} else if (dbCertPem) {
authOptions = getAuthOptionsFromCertPem(dbCertPem);
}
store = new DocumentStore(urls, databaseName, authOptions);
if (customize) {
customize(store.conventions);
}
store.initialize();
initialized = true;
return store;
}
async function getAuthOptionsFromCertificatePath(
dbCertPath,
dbCertPassword
) {
return {
certificate: await readFile(dbCertPath),
password: dbCertPassword,
type: "pfx",
};
}
function getAuthOptionsFromCertPem(dbCertPem) {
let certificate = dbCertPem;
const isMissingLineEndings = !dbCertPem.includes(EOL);
if (isMissingLineEndings) {
// Typically when pasting values into Azure env vars
certificate = normalizePEM(certificate);
}
return {
certificate,
type: "pem",
};
}
function normalizePEM(pem: string): string {
return pem.replace(PEM_REGEX, (match, certSection, certSectionBody) => {
const normalizedCertSectionBody = certSectionBody.replace(/\s/g, EOL);
return `-----BEGIN ${certSection}-----${EOL}${normalizedCertSectionBody.trim()}${EOL}-----END ${certSection}-----${EOL}`;
});
}
const PEM_REGEX =
/-----BEGIN ([A-Z\s]+)-----(\s?[A-Za-z0-9+\/=\s]+?\s?)-----END \1-----/gm;
export function openDbSession(opts) {
if (!initialized)
throw new Error(
"DocumentStore is not initialized yet. Must `initializeDb()` before calling `openDbSession()`."
);
return store.openSession(opts);
}This supports using .pfx files or a PEM-encoded certificate, if provided.
It normalizes the PEM value if it does not contain line endings.
Load from Azure Key Vault
Azure Key Vault is a paid service that allows you to store, retrieve, and rotate encrypted secrets including X.509 Certificates. This is recommended for more robust certificate handling.
Using the SecretsClient, you can load secrets from Key Vault.
However, you will need to use the CertificateClient to retrieve a certificate from the vault.
For more, see the sample code for using CertificateClient.
Configuring Azure
You will need to configure certificate authentication in Azure. Depending on the method you choose above, the steps vary.
Specifying Path to Certificate
If you are deploying a physical .pfx file, you can specify the DB_CERT_PATH and DB_PASSWORD app settings.
Specifying PEM Certificate
If you are loading a PEM-encoded certificate, follow the steps below to make your .pem certificate available to your Azure Functions:
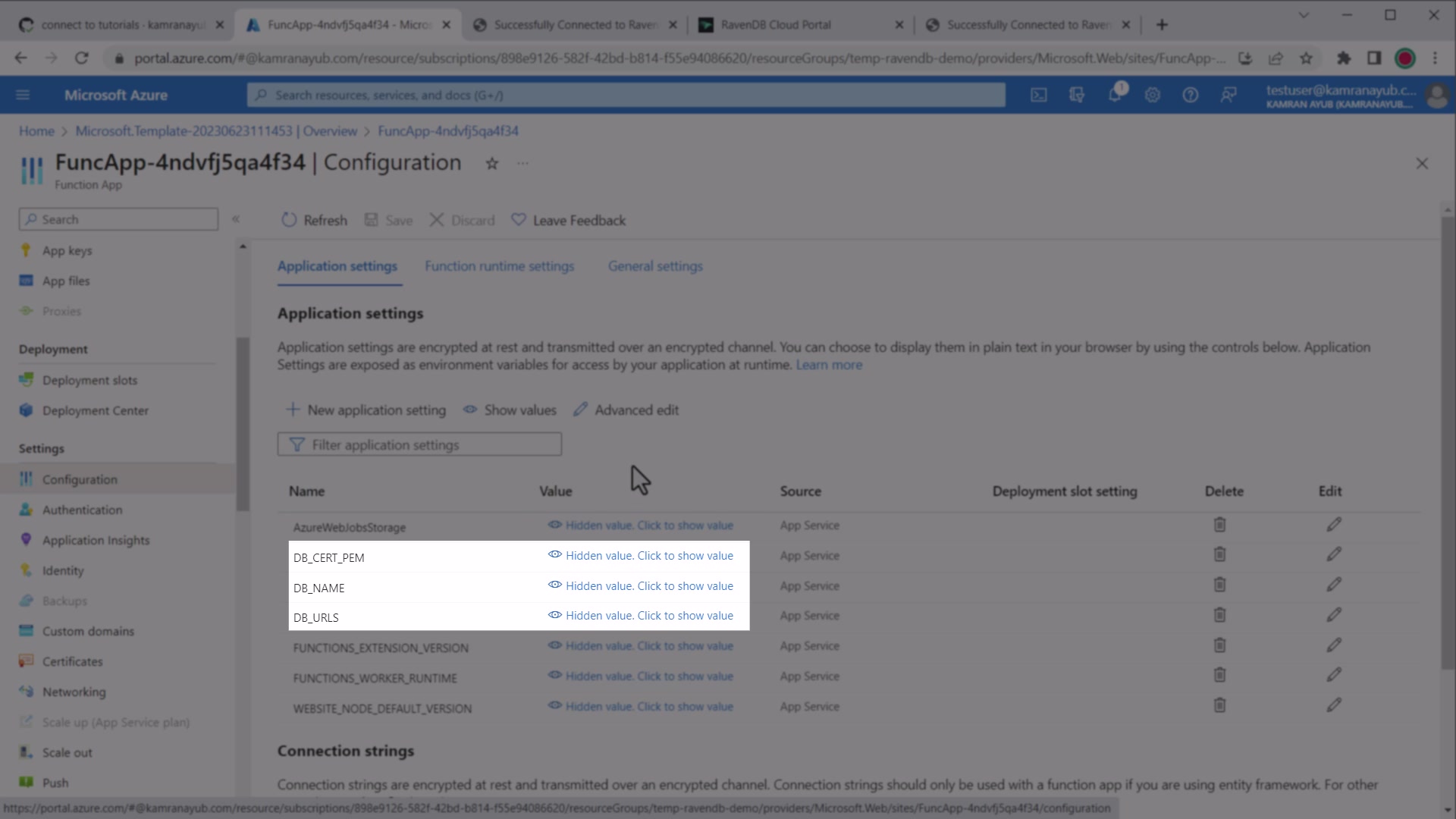
.NET update Azure app settings
- Find the
.pemcertificate provided by RavenDB client certificate package - Copy its full contents
- Go to your Azure Functions dashboard in the Portal
- Click the Application Settings menu
- Modify or add the app setting for
DB_CERT_PEMand paste the contents of your.pemfile
These values will override local.settings.json once deployed on Azure.
Next Steps
- Learn more about how to use the RavenDB Node.js client SDK
- Reference the Node.js Azure Function starter template to see the code
- Troubleshoot issues with RavenDB and Azure Functions
- Deployment Considerations for RavenDB and Azure Functions